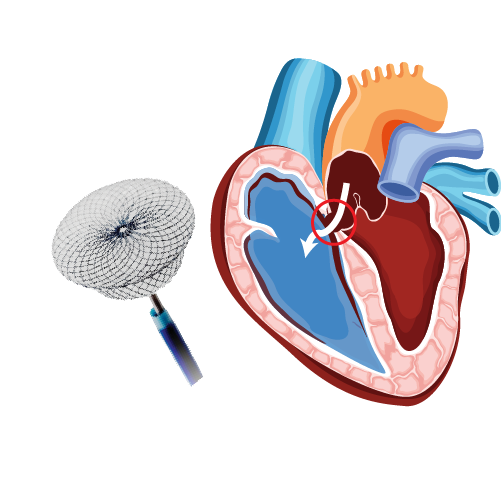
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy is a genetic disorder, where the muscle wall (septum) between the lower chambers of heart, thickens abnormally resulting in improper functioning of the heart.
It’s often undiagnosed due to lack of significant clinical manifestations.
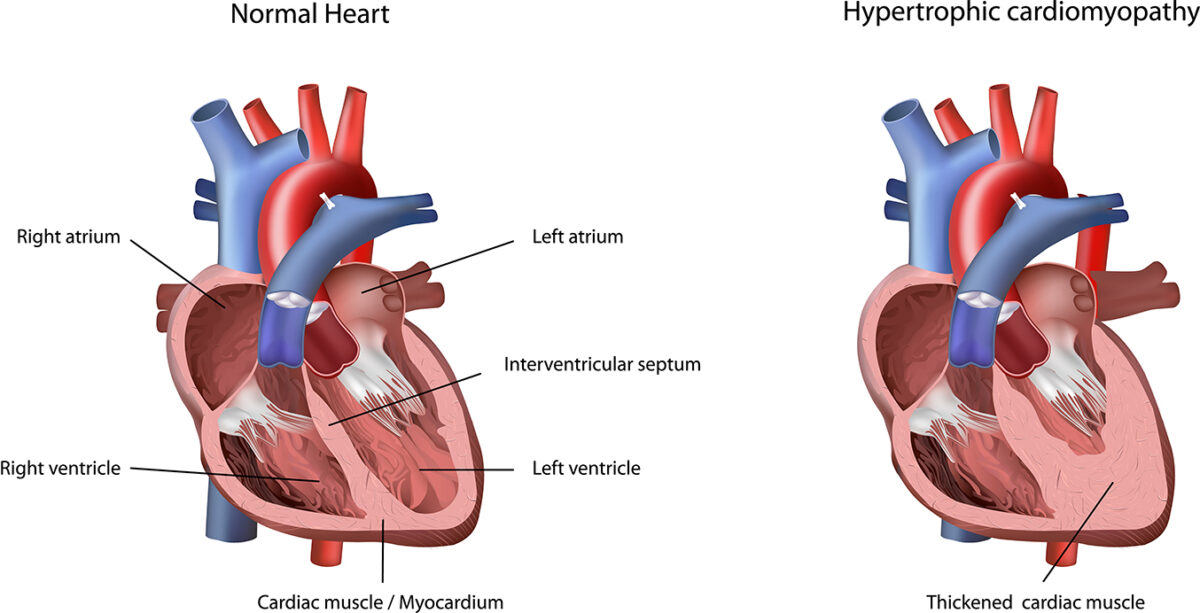
What are the symptoms of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
- Shortness of breath, especially during exercise or lying position
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Fainting during physical activity
- Fatigue
- Swelling in legs, feet or ankles
What are the causes of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
- Older age
- High blood pressure
- Gene mutations (inherited)
Who are at risk of developing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
- Family history of Cardiomyopathy
- Severe obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- Alcohol intake
- Certain heart diseases such as sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis or amyloidosis
What are the consequences of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy?
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
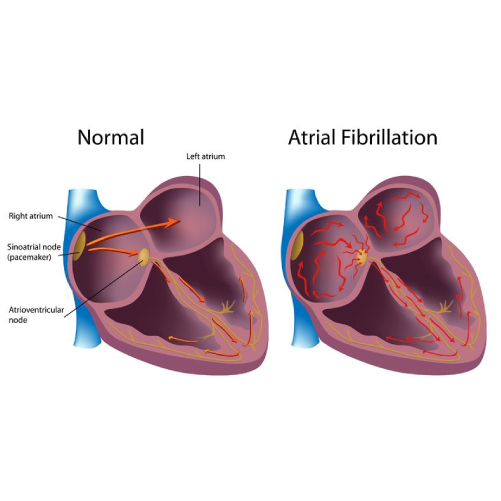
- Atrial fibrillation
- Improper blood flow
- Mitral valve problems
- Heart failure
- Sudden cardiac death
How is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy diagnosed?
- Echocardiogram: This is commonly used to diagnose Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Utilizes ultrasounds to see abnormally thickened heart muscle. It also examines heart chambers and valves.
- Electrocardiogram: To measure electrical signals of the heart.
- Cardiac MRI
- Exercise test: Record’s EEG while treadmill or physical activity
- Genetic testing for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: To identify the gene mutation
How is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy treated?
Non-pharmacological treatment:
- ICD (Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator)
- Septal ablation (Catheter-based therapy)
- Septal myectomy (Surgery based therapy)
- A pacemaker in case of abnormal heartbeat
Pharmacological treatment:
- Anticoagulants such as warfarin, rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban in case of atrial fibrillation to prevent blood clots
- CCB’s( Calcium channel blockers) such as verapamil or diltiazem
- Beta-blockers such as metoprolol, propranolol or atenolol
Amiodarone or disopyramide to control over heart rhythm
Our Specialities
- Conditions
Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis
Diagnosis
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT

Dr. RAGHU
MD, DM, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
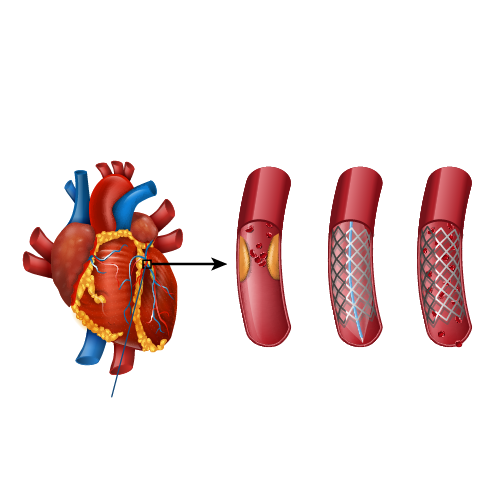
Angioplasty
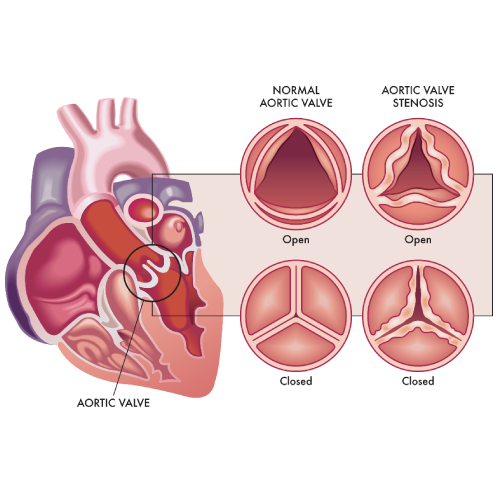
Aortic Stenosis
Atrial Fibrillation