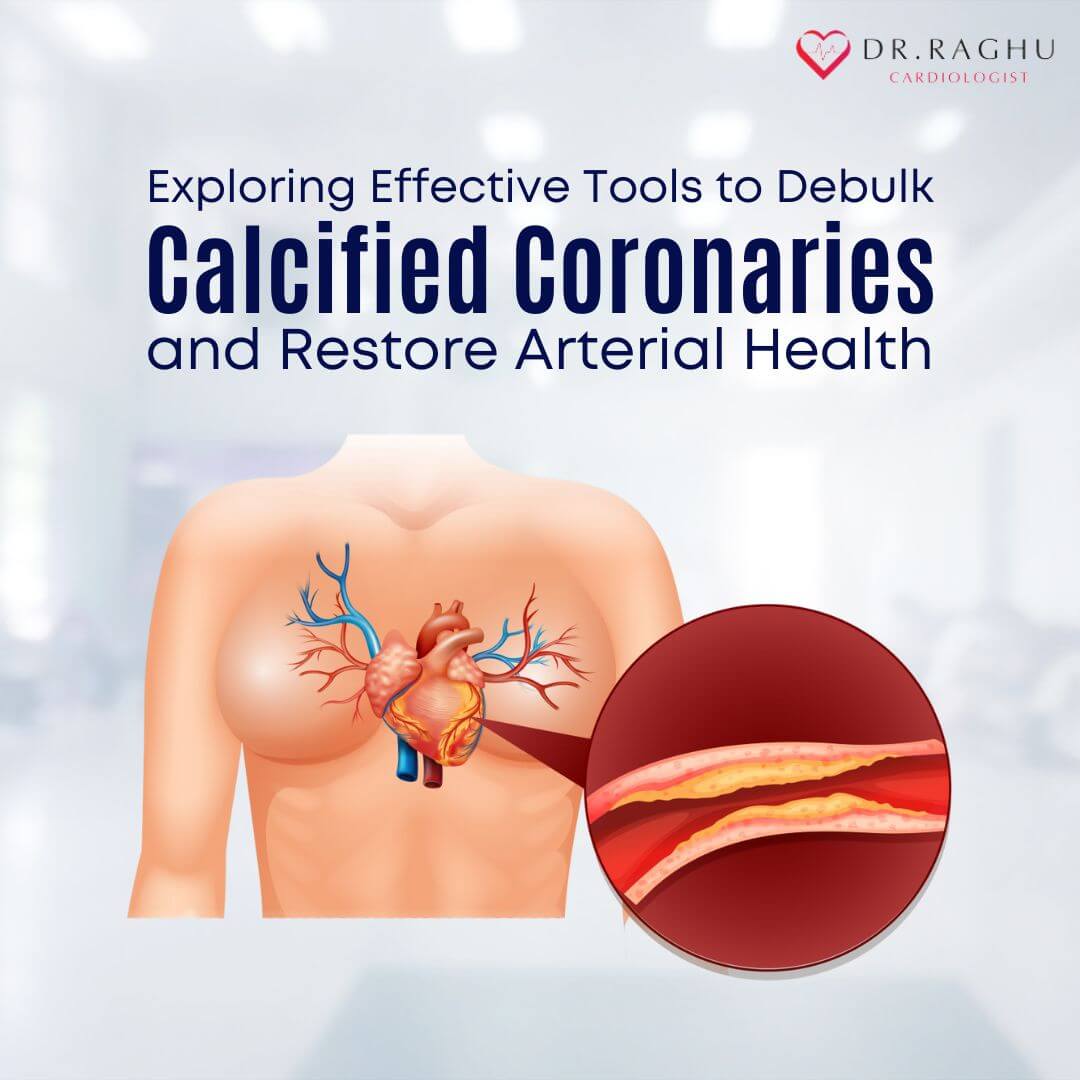
Cardiovascular diseases continue to be a leading cause of mortality globally, with calcified coronary arteries posing a significant challenge in interventional cardiology.
angioplasty | Dr Raghu
Metal free PCI represents a significant shift in the domain of interventional cardiology. This innovative approach eliminates the need for traditional metal stents and offers several benefits over traditional PCI.
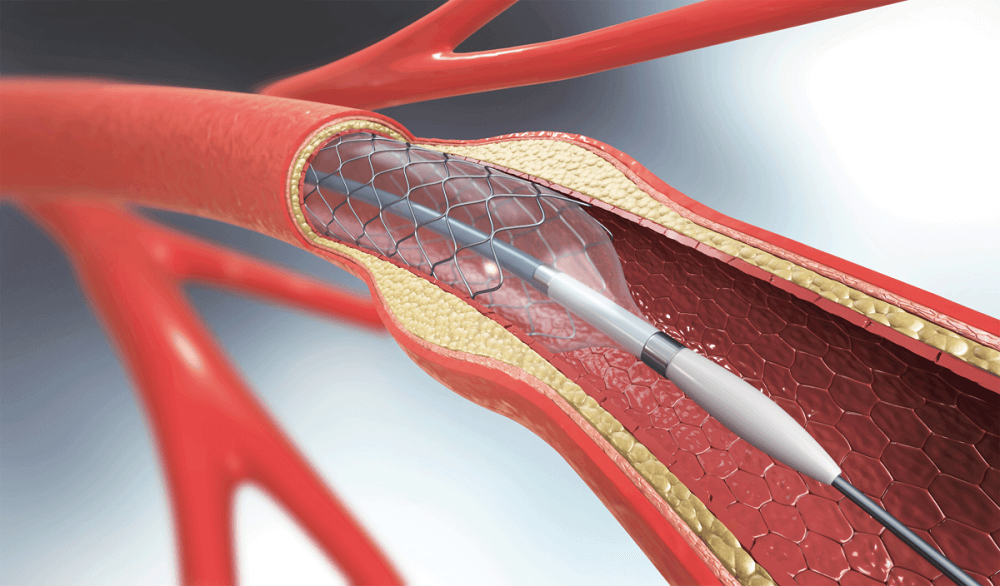
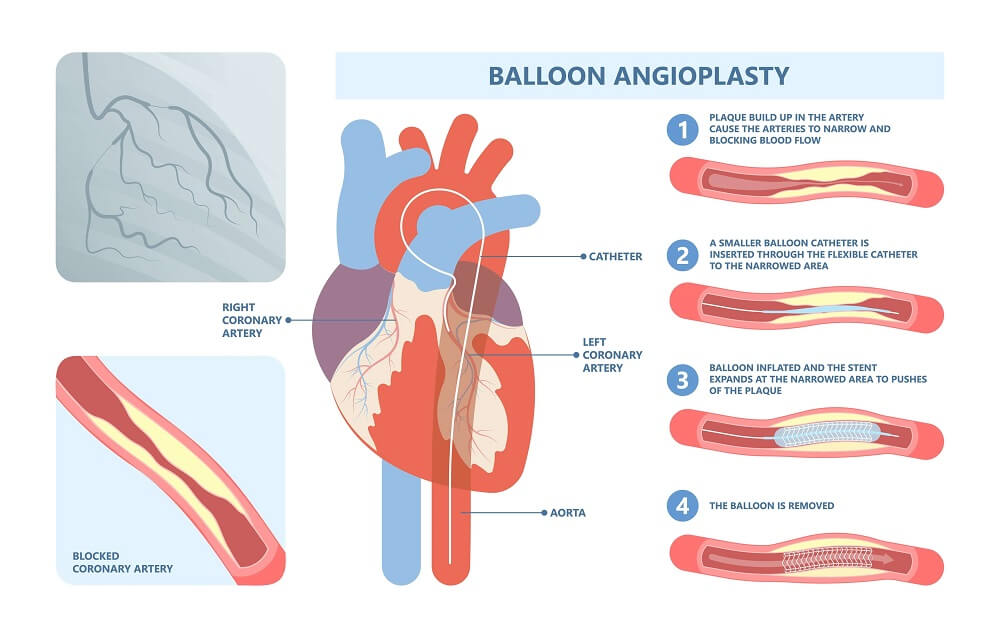
Angioplasty is a medical procеdurе usеd to trеat narrowed or blocked blood vessels, typically arteries lеading to thе hеart. It’s performed to rеstorе propеr blood flow to thе hеаrt muscle and alleviate symptoms such as chеst pain (angina) or prеvеnt heart attacks.
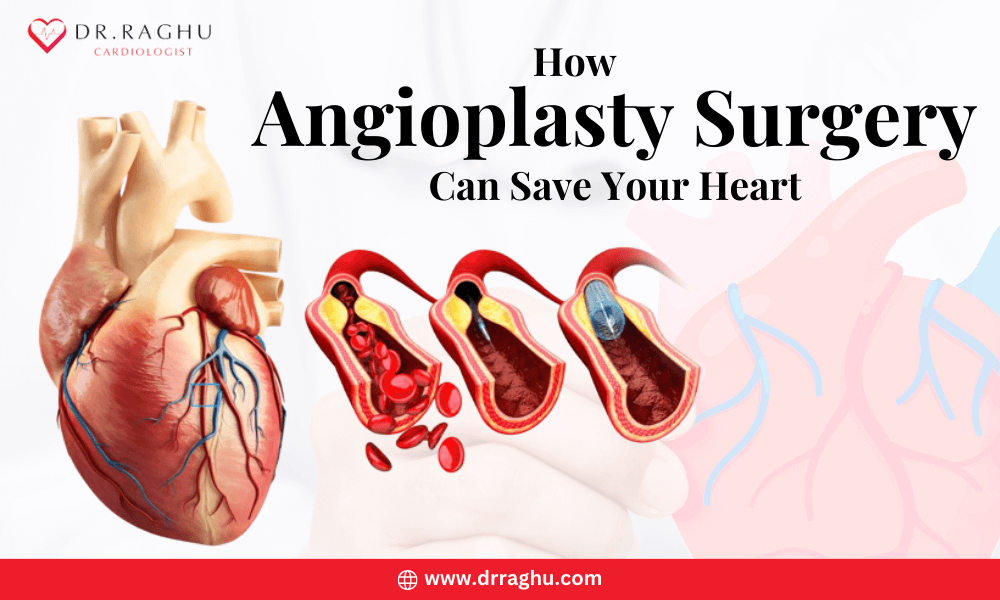
Angioplasty in the heart has emerged as a crucial lifesaving procedure for those suffering from heart-related issues.
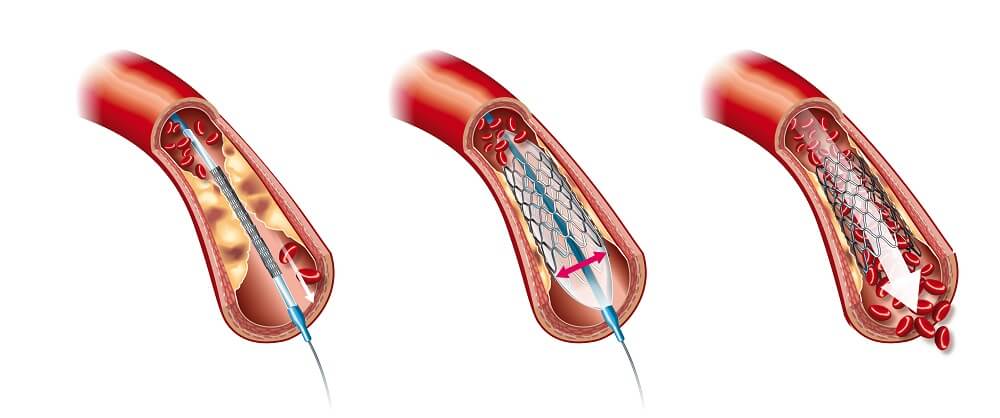
Angioplasty and stent placement are interventional cardiology procedures commonly used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). These procedures work together to restore blood flow to the heart muscle by widening narrowed or blocked arteries.
Angiography and angioplasty in the heart are two different procedures. Angiography is a diagnostic tool used to identify blockages, while angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure used to open up blocked blood vessels.
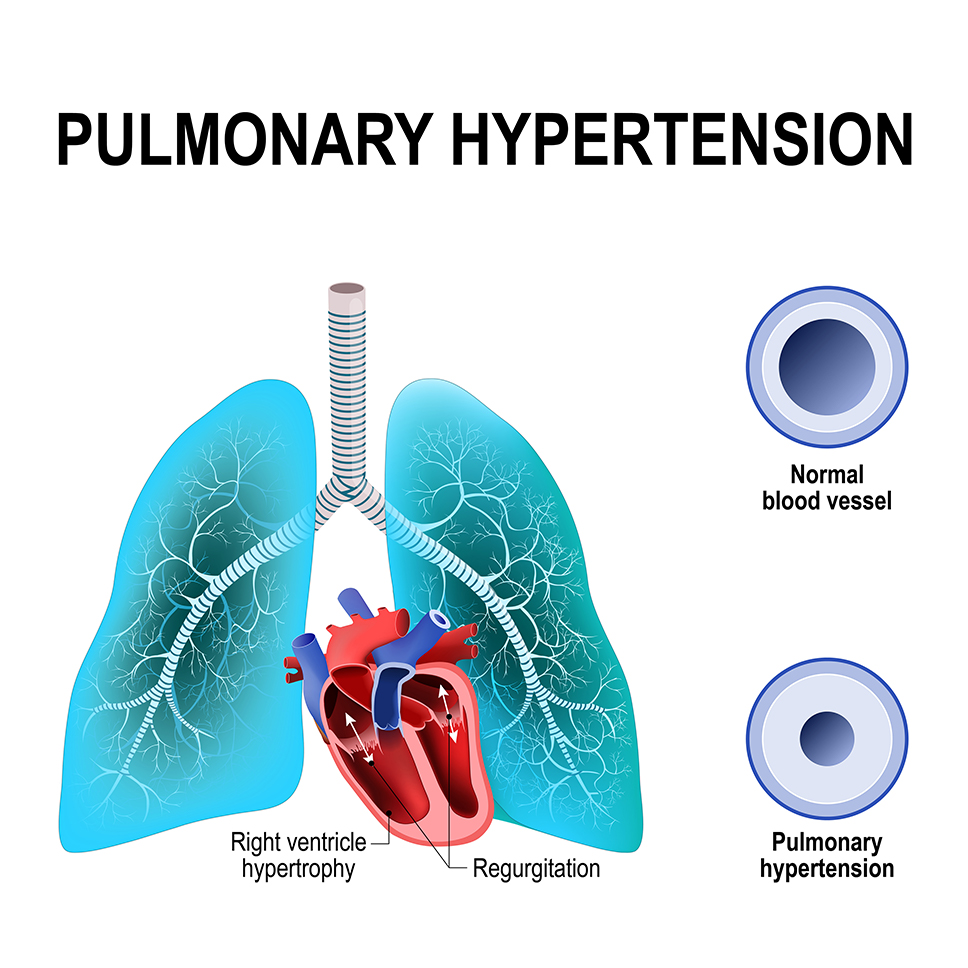
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) is a rare form of pulmonary hypertension that occurs when blood clots, or thrombi, form in the arteries of the lungs and do not fully dissolve.