Varicose Veins
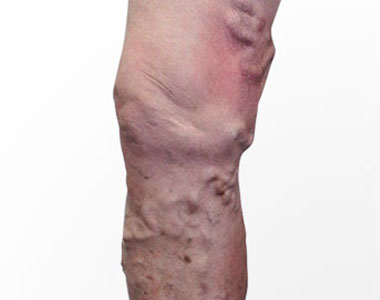
Varicose veins are the twisted, swollen and bulging veins that appear in blue, red and skin color, just beneath the surface of the skin. They occur mostly in the legs and feet, causing aching pain and discomfort in the legs.
Larger varicose veins appear rope-like and make the skin to bulge out. Inner varicose veins usually do not appear, but cause aching pain and swelling in the legs. Spider veins are the type of varicose veins which are most common and occur superficially, surrounded by the patches of flooded capillaries.

Causes:
Arteries have a thick layer of muscle or tissue to supply oxygenated blood to different parts of the body. Veins carry blood back to the heart and it should work against the gravity, so they rely on surrounding muscles pressure. Valves in the veins open to move the blood towards the heart and then close to prevent the back flow of blood.
Any damage/abnormality in the functioning of the valves will lead to pooling up of blood in the vessels, causing them to stretch and twist, resulting in varicosity. It mostly occurs due to prolonged standing and walking, which builds up pressure in the veins of the lower legs.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Dark purple or blue color veins
- Twisted and bulging veins that appear on the surface of the skin
- Aching pain and heaviness in the legs
- Burning, throbbing, muscle cramping and swelling in the lower legs
- Worsened pain after sitting or standing for a long time
- Itching around affected veins
- Skin discoloration around a varicose vein
- Web-like reddish blue varicose veins called spider veins
Risk factors:
The factors that increase the risk of developing varicose veins are:
- Age: As the age increases, the functioning of the valves in the veins may be damaged, resulting in pooling up of blood in the lower leg veins, leading to varicose veins.
- Gender: Hormonal changes in women during pregnancy, premenstruation and menopause will relax the vein walls, which increases the risk for varicose veins. Use of hormonal birth control pills also increases the risk.
- Pregnancy: Blood volume increases during pregnancy to support the developing fetus, but can also produce a side effect of enlarged veins.
- Family history: If any family member has varicose veins or deep vein thrombosis, it increases the risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight will increase the pressure in the veins of lower legs.
- Standing or sitting for long periods of time will reduce the free flow of blood in the blood vessels and results in clot formation.
Complications:
- Ulcers: Skin ulcers may form near the ankle, which is an indication of vascular disease.
- Blood clots: Clots may occur in the veins deep inside the legs, causing swelling and leg pain. The condition is referred as thrombophlebitis.
- Bleeding: Sometimes, the superficial veins may burst, causing bleeding.
Diagnosis:
A physical examination is performed, and the patient is enquired about the nature of leg pain diagnose varicose veins. The family medical history of varicose veins and information about their daily lifestyle activities is gathered. Certain tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis of varicose veins, and include:
- Ultrasound test: This is a non-invasive test, which uses sound waves to create the images of internal organs of the body. This test helps to identify the blood flow in the veins and also identify the clots and weakened or leaky valves in the veins.
- Venogram: This test is a type of angiogram, which uses contrast dye to clearly view the blood flow through the veins, mainly if physician suspects the presence of large clots in the veins.
Treatment:
Initially, after the diagnosis of varicose veins, the doctor would recommend some lifestyle modifications that can relieve pain and reduce worsening of the condition, such as:
- Perform exercises
- Elevate the legs.
- Avoid tight fitting clothes that can prevent the free circulation
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting
Compression stockings: It will compress the leg veins and muscles and improve the blood flow efficiently, without forming any clots in the veins. The stockings are available in different sizes and lengths and can be bought without prescription in the local pharmacy.
Sclerotherapy: This procedure is mainly used for severe varicose veins, and involves injecting a chemical solution near the varicose veins, which helps in closing and scarring of the veins.
Laser treatment: This technique uses bursts of light reflected onto the vein, which makes the vein slowly fade and disappear. This test is mainly used to treat smaller varicose veins.
Catheterization: This procedure uses a thin, flexible tube (catheter) that is inserted into the enlarged vein, which uses radiofrequency or laser energy, mainly to collapse the larger varicose veins.
High ligation and vein stripping: Veins are tied off before it joins a deep vein and then it is removed through an incision.
Ambulatory phlebectomy: Series of small punctures are made in the skin under general anaesthesia, to remove the smaller varicose veins.
Endoscopic vein surgery: A thin tube attached with a camera is inserted into the vein to view and close the varicose veins and then removing them by making small incisions on the skin, under general anaesthesia.
Prevention:
Varicose veins cannot be prevented completely, but can be reduced by following some measures like:
- Exercising regularly and losing extra weight
- Eating a high-fiber and low-salt diet
- Avoiding high heels and tight hosiery
- Elevating the legs.
- Changing the position regularly, when sitting or standing for long periods

