Atrial Fibrillation (Afib) – Cause, Symptoms, Complications & Treatment
What is atrial fibrillation (Afib)?
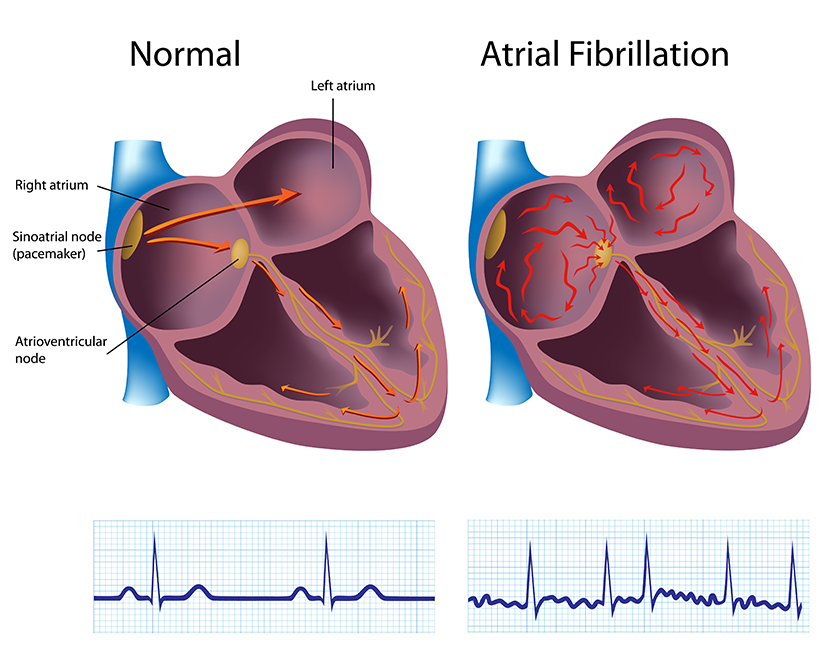
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular or fast beating of upper chambers (atria) of heart leading to ineffective blood pumping to various organs.
Atrial fibrillation is termed as “A-fib” in short form.
This condition increases the risk of developing stroke; heart-related problems as well as death due to the blood clots formed during an irregular heartbeat.
Atrial fibrillation is classified into different categories include:
- Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (paroxysmal afib): Irregular heartbeat terminates immediately or with intervention within seven days.
- Persistent atrial fibrillation: This stage cannot be self-terminate by itself and require medication or electrical shock for the restoration of normal rhythm and rate.
- Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: Symptoms lasting more than 12 months.
- Permanent atrial fibrillation: In this type, atrial fibrillation is not restored permanently and often requires lifelong medicines to control rate and rhythm.
What are the atrial fibrillation causes?
- Hypertension (High blood pressure)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Heart-related problems like heart valve disease, coronary artery disease, congenital heart disease.
- Diabetes mellitus (High sugar levels)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Chronic lung disease
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Who increases the risk of developing atrial fibrillation (Afib)?
- Older age
- Previous heart disease/heart surgery
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Metabolic disorders
- Family history of atrial fibrillation
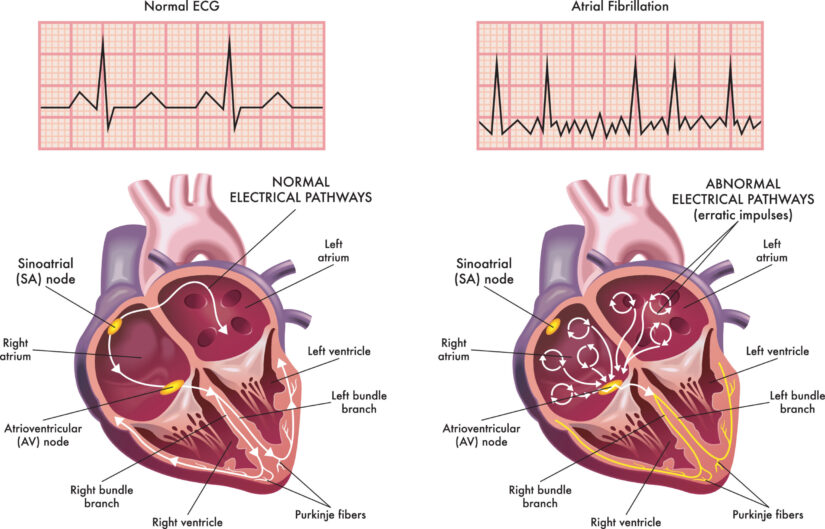
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Lightheadedness and dizziness
- Sweating
- Syncope
- Fatigue
What are the complications of atrial fibrillation (afib)?
- Stroke: In atrial fibrillation, the abnormal rhythm may use the overload of blood in atria and form blood clots. These clots potentially can travel into blood vessels the brain and cause stroke.
- Heart failure: When the heart cannot pump blood enough to meet body metabolic requirements.
- Cardiac myopathy: Weakness of cardiac muscle
- Sudden death
How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed?
- Electrocardiogram: To determine electrical changes in heart during atrial fibrillation
- Echocardiogram
- Transthoracic echocardiogram
- CT scan
- Chest X-ray
How is atrial fibrillation treated (Afib)?
- Anti-coagulation therapy to prevent blood clots
- Pharmacological therapy to control heart rate and rhythm
- Electrical cardioversion ( Shock) to reset the cardiac rhythm
- Cardioversion with antiarrhythmic rhythmics to restore cardiac rhythm
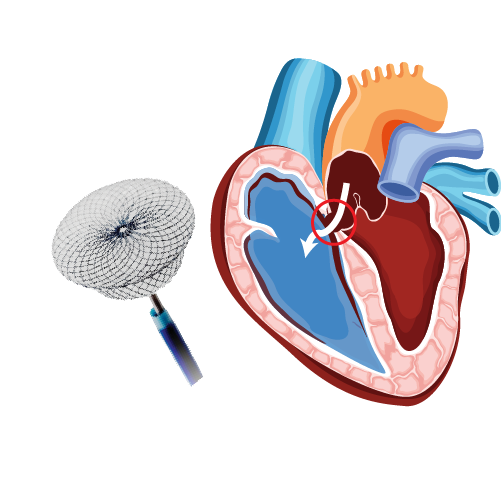
- Catheter ablation/maze procedure/ AV node ablation to restore normal rhythm
Left atrial appendage closure to prevent blood clots
Our Specialities
- Conditions
Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis
Diagnosis
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT

Dr. RAGHU | Best Atrial Fibrillation Doctors in India
MD, DM, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
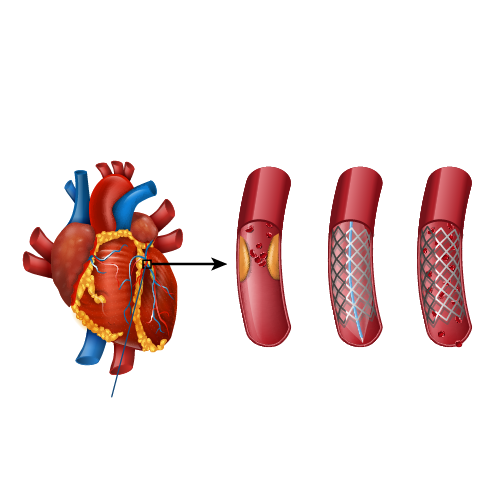
Angioplasty
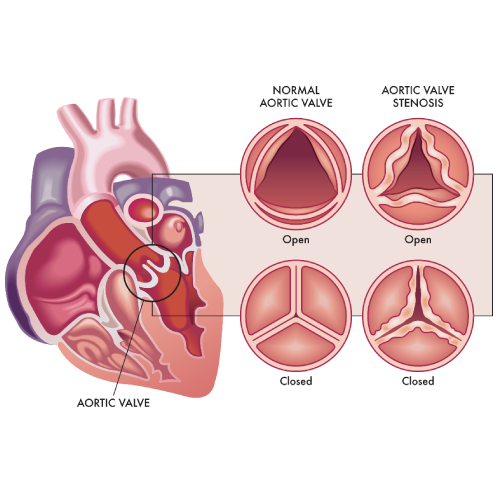
Aortic Stenosis
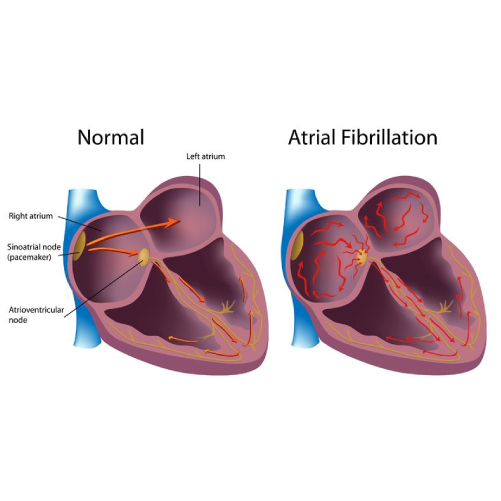
Atrial Fibrillation