High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
What is high blood pressure?
- The amount of force that blood put against the artery wall to circulate throughout the body is called blood pressure
- High blood pressure occurs when the blood flows through arteries with high pressure than normal. It is termed Hypertension.
- Hypertension is classified into two different categories:
- Primary Hypertension: Also called essential hypertension, where there is no known cause. This type of hypertension develops slowly due to lifestyle, environment, or age.
- Secondary Hypertension: This type of hypertension is secondary due to health problem or medicine.
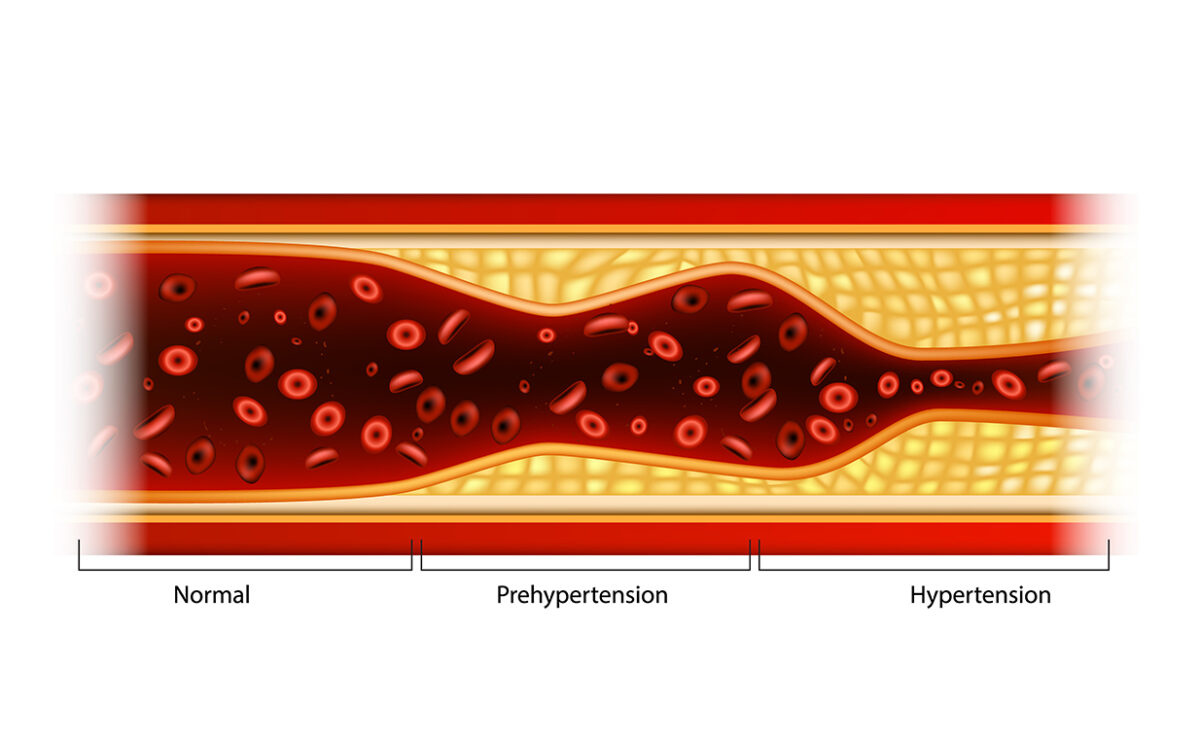
How is high blood pressure classified?
| Blood pressure Category | Systolic blood pressure | Diastolic blood pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Blood Pressure | Less than 120 | less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120 – 129 | less than 80 |
| Hypertension (Stage 1) | 130 – 139 | 80 – 89 |
| Hypertension (Stage 2) | 140 or Higher | 90 or Higher |
| Hypertensive crisis | Higher than 180 | Higher than 120 |
What are the high blood pressure symptoms?
High blood pressure has rarely noticeable symptoms includes:
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Nose bleeding
What are the risk factors of high blood pressure?
- Elderly age
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- High salt or potassium in the diet
- Stress
- Family history
- Certain chronic diseases like kidney damage, sleep apnea, or diabetes
What are the complications of high blood pressure?
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Aneurysm
- Dementia
- Metabolic syndrome
- Narrowed blood vessels in kidneys
- Narrowed blood vessels in eyes
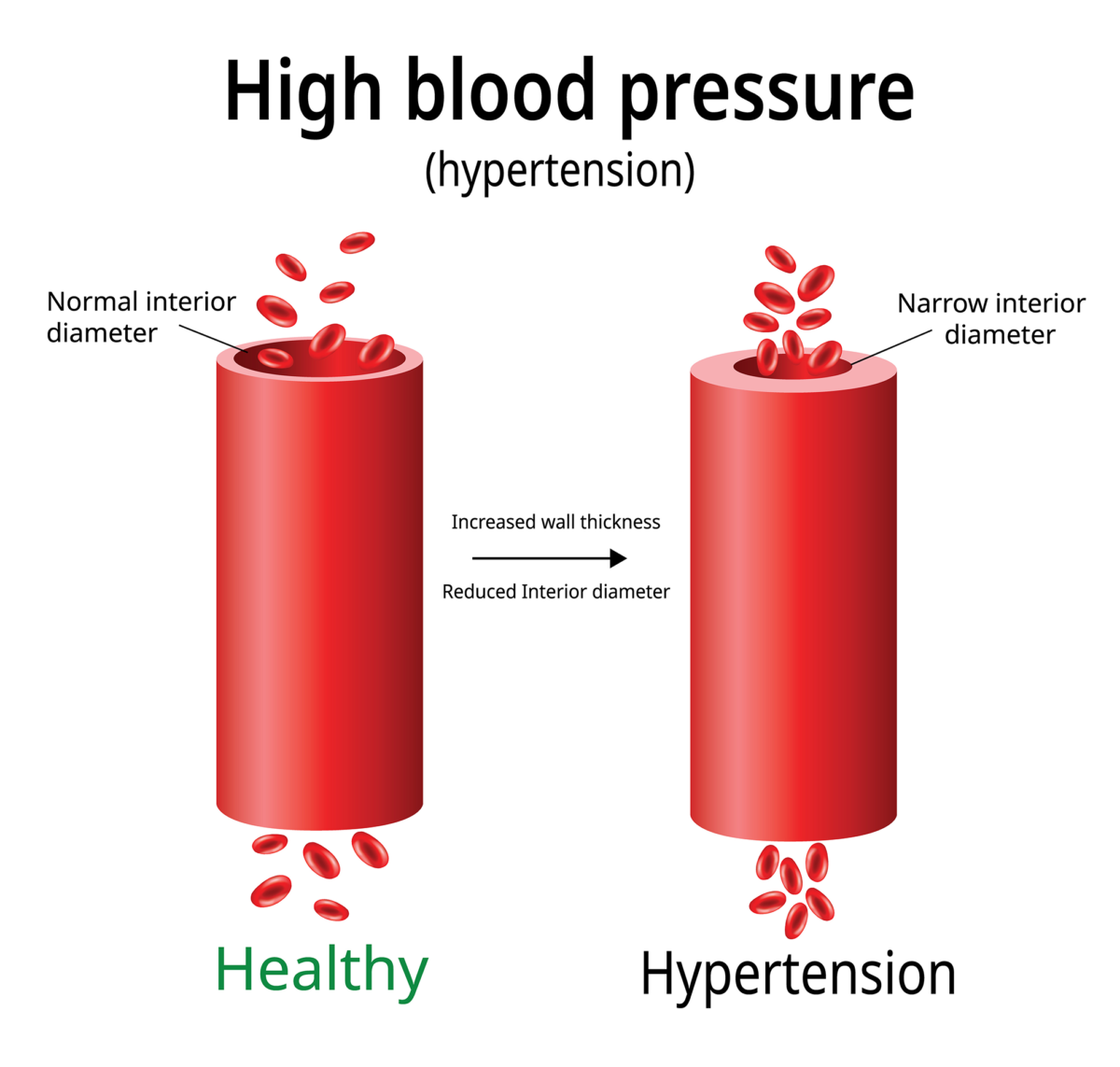
How is high blood pressure diagnosed?
- Sphygmomanometer, a digital electronic monitor which is connected to the inflatable cuff that used to wrap the upper arm measures the blood pressure.
- During blood pressure is the measurement, the reading is recorded into two different numbers (systolic/diastolic mmHg).
- Systolic pressure: The highest level of blood pressure when heartbeats and contracts to pump blood through arteries.
- Diastolic pressure: Lowest level of blood pressure when the heart relaxes between beats.
How is high blood pressure treated?
- Diuretic acts on kidneys to help in eliminating excess sodium and water from the body
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE’s) inhibitors: For relaxation of blood vessels
- Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB’s): For relaxation of blood vessels
- Calcium channel blockers
What is your target blood pressure?
- In adults with confirmed Hypertension (High blood pressure) and a known case of Cardiovascular disease, targeted Blood pressure should be less than 130/80 mmHg
- In adults with confirmed Hypertension (High blood pressure) and no risk of Cardiovascular disease, targeted Blood pressure is less than 130/80 mmHg
- In patients > 80 years, the targeted Blood pressure should be less than 150/90 mmHg
- In patients < 80 years, the targeted Blood pressure should be less than 140/80 mmHg
- For patients with Diabetes and younger than 70 years, targeted Blood pressure is less than 130/80 mmHg
- For patients with Diabetes and lies in 70 to 80 years, targeted Blood pressure is less than 140/90 mmHg
For patients with Diabetes and older than 80 years, targeted Blood pressure is less than 150/90 mmHg
Our Specialities
- Conditions
Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis
Diagnosis
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT

Dr. RAGHU | Hypertension Treatment in Hyderabad
MD, DM, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
Angioplasty
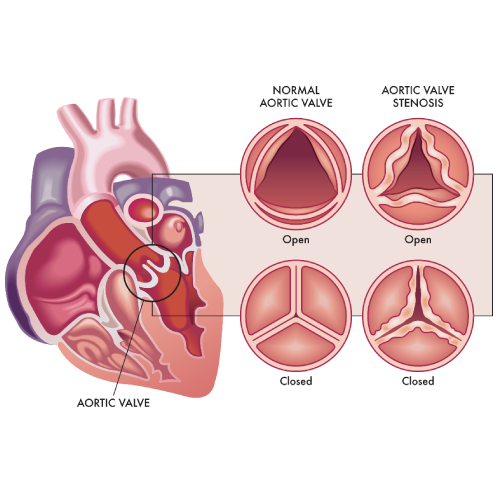
Aortic Stenosis
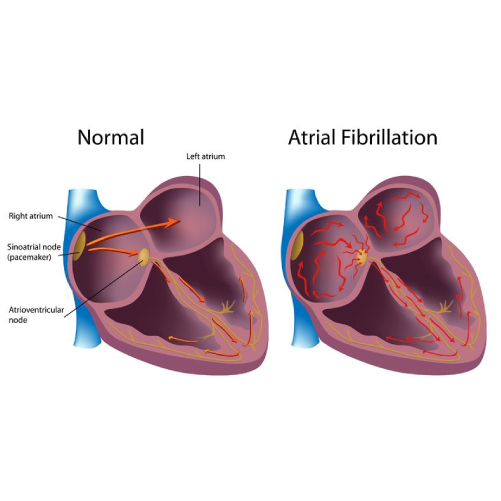
Atrial Fibrillation