Atrial Fibrillation And The Heart’s Rythm
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is one of the most common heart arrhythmias (irregular or abnormal beating). It happens when your heart’s upper chambers (the atria) beat abnormally fast and out of rhythm. It can lead to severe complications like blood clots, stroke, and heart failure. So you must know how AFib affects your body and what to do about it.
The Heart Is a Smart Pump
The heart is a muscular organ that’s divided into four chambers. The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium and ventricle, and the mitral valve separates the left atrium and ventricle. The heart can’t just pump blood around your body; it also has to know what’s going on and how to respond. The heart can do this because of the electrical system within its walls.
The heart’s electrical system is made up of two different types of cells: pacemaker cells and conducting cells. The pacemaker cells are found in the upper right chamber. They generate an electrical impulse that travels through the conducting system to stimulate the contraction of your ventricles (right and left).
Beating of a Heart
A heartbeat is caused by electrical signals traveling through the heart chambers and valves to tell them how hard to contract at what time. The sinoatrial node (SA node) sends these signals out; it’s located at the junction of your right atrium and superior vena cava. The SA node acts as the central command for your cardiac rhythm. It keeps track of all your electrical activity and coordinates how to pump blood efficiently throughout the body.
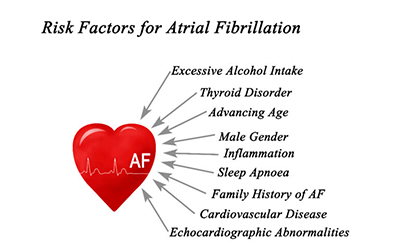
What Happens in Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disorder where abnormal electrical signals from an overactive nerve cause the atria to contract too quickly and chaotically, which causes blood to pool in the upper chambers of your heart instead of flowing smoothly into the ventricles.
It can lead to symptoms like:
- Palpitations (heart pounding)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Sweating
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common type, is a temporary condition that can last a few minutes or several days. When you have paroxysmal AF, you may experience symptoms such as heart palpitations and shortness of breath. Some people also experience chest pain or lightheadedness in addition to the above symptoms.
Persistent atrial fibrillation is an ongoing condition with abnormal heart rhythms that last longer than three months. But it’s not considered chronic AFib if you don’t experience any symptoms from them.
Permanent atrial fibrillation is another type of long-term irregular heartbeat that occurs when all the cells in your heart’s upper chambers develop arrhythmias (irregular electrical signals) for an extended period.
Conclusion
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that can be serious. It’s important to know the symptoms of atrial fibrillation and how you can manage it. If you think you have atrial fibrillation, contact your doctor right away so they can help diagnose and treat the condition before it gets worse!

