Deep Vein Thrombosis
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition in which blood clot forms in the deep veins such as lower leg, thigh or arm vein due decrease in the blood flow rate. This condition is dangerous when the clot breaks and travels to the lungs through the bloodstream that leads to a serious and life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism.

What are the causes of DVT?
- Injury to deep vein
- Slowed blood flow
- Inherited clotting disorder
- Medications such as oral contraceptive pills
Who are at risk of developing DVT?
- Obesity
- Older age
- Standing/sitting in a place for long periods
- Lack of physical activity
- Pregnant or Lactating women
- Estrogen supplements
- Hospitalized patients
- Smoking
- History of the following :
- Clotting disorder
- Carcinoma
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Cardiovascular disease
- Genetic conditions where Factor V Leiden is mutated
- Neurological diseases like paralysis
What are the symptoms of DVT?
- Swelling, pain or tenderness in the arm or leg
- Warmth, redness or discolouration in the arm or leg
- Enlarged veins
- Leg cramps
What are the complications of DVT?
- Pulmonary embolism: Requires medical attention.
- Symptoms include :
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness
- Increased heart rate
- Haemoptysis
- Postphlebitic syndrome: Common complication after Deep Vein Thrombosis.
- Symptoms include:
- Oedema
- Skin discolouration
- Ulcers
- Pain or discomfort in legs
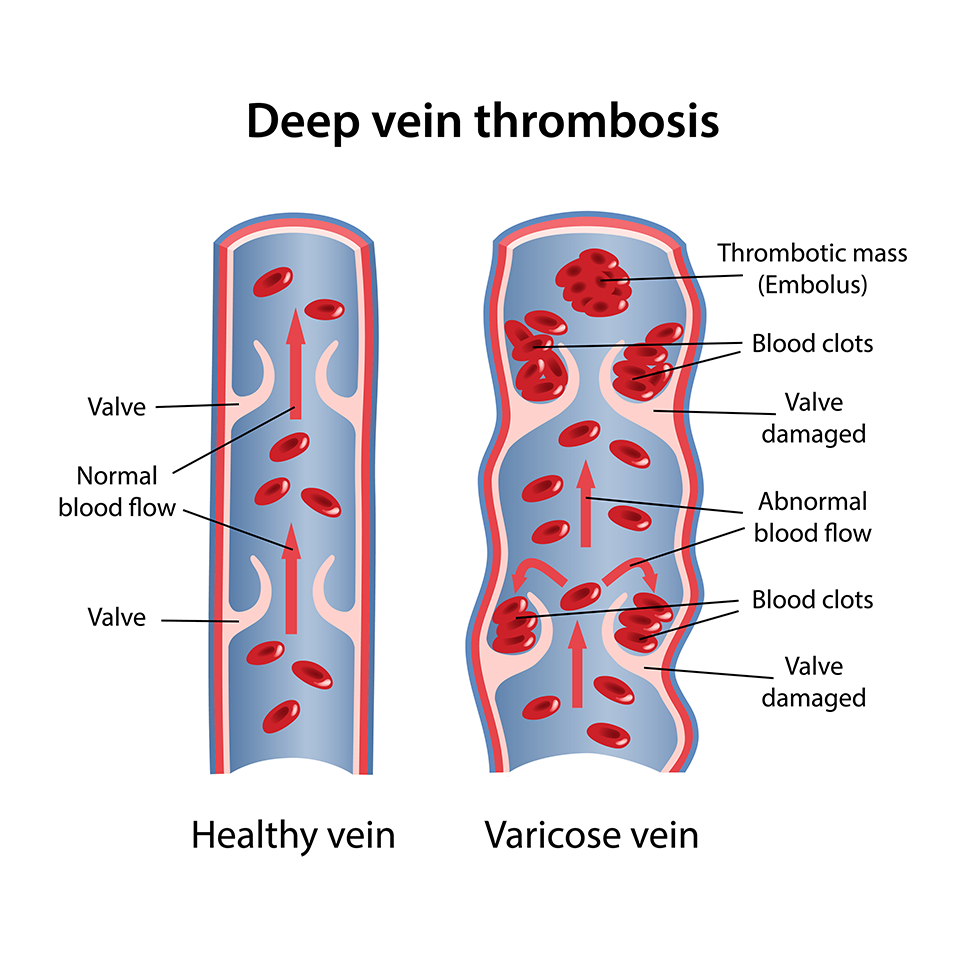
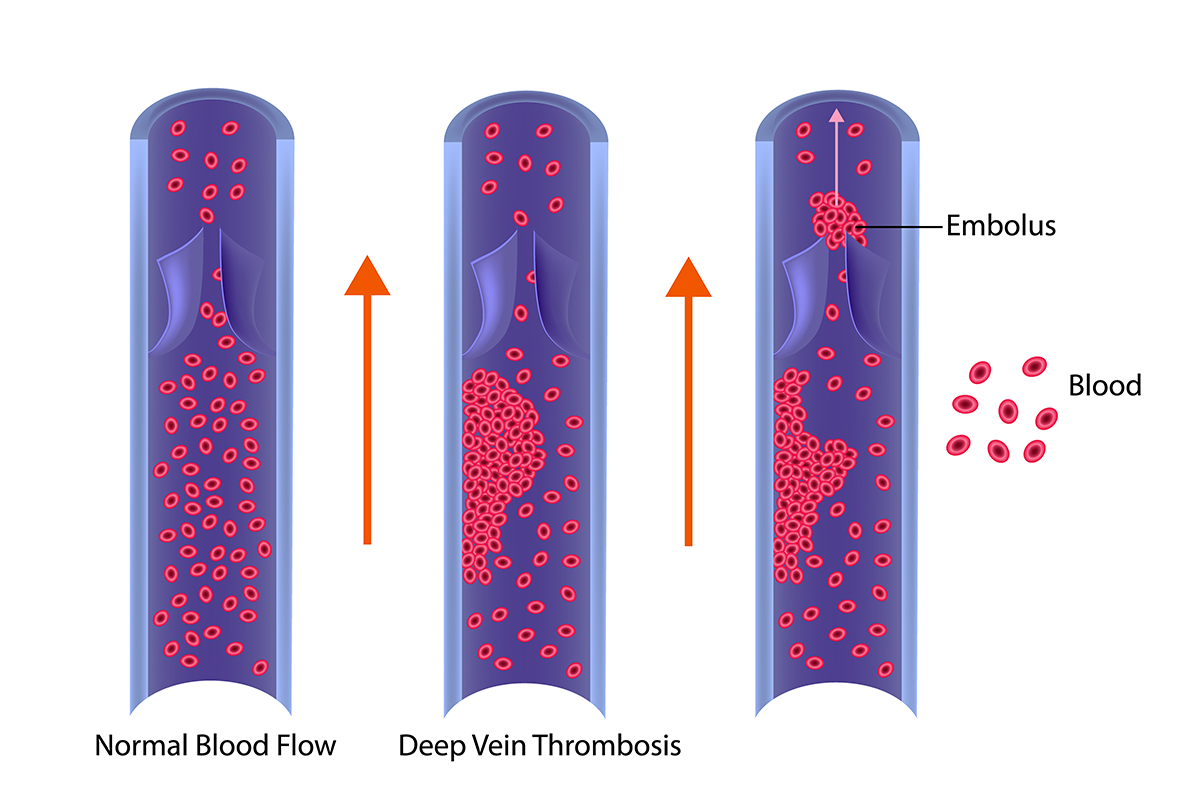
How is DVT diagnosed?
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Blood test: to check for clotting factor
- Ultrasound: to check for clots
- Venogram: During this test, a contrast dye is injected into vein and X-rays are taken for observing the presence of clots.
How DVT is treated?
- Blood thinners such as anticoagulants (Heparin, warfarin, enoxaparin or fondaparinux) to dissolve the clot.
- In severe conditions of DVT, thrombolytic agents (streptokinase, urokinase, tissue plasminogen activator) prescribed for breaking the clots through a catheter (Catheter-directed thrombolysis).
- Surgery to remove the clot
Precautions for DVT:
- Avoid over the counter drugs
- Avoid aspirin or NSAIDs during anticoagulant therapy
- Avoid usage of estrogen supplements
Lifestyle Modifications for DVT:
- Lose weight
- Avoid standing or sitting for a long duration
- Quit smoking
- Exercise daily to reduce the risk of developing clots
Drink plenty of water
Our Specialities
- Conditions
Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis
Diagnosis
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT

Dr. RAGHU
MD, DM, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
Angioplasty
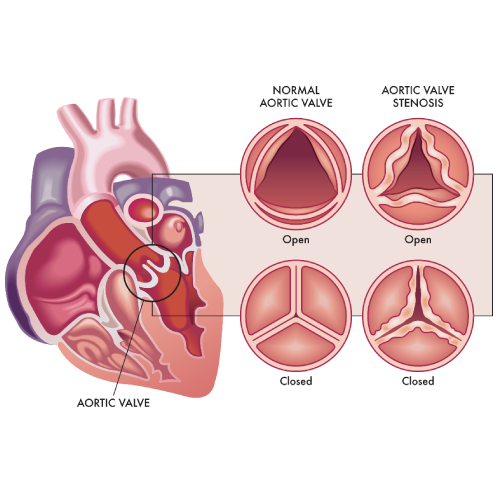
Aortic Stenosis
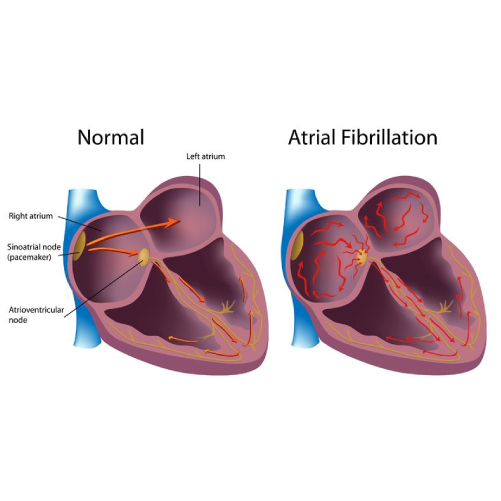
Atrial Fibrillation