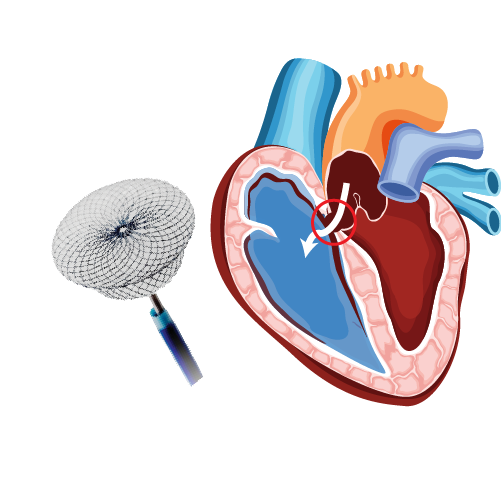
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter
What is IVC filter placement procedure?
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE), deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) affects 1 to 2 individuals per 1,000 annually
- These are the leading cause of preventable hospital death
- DVT is more commonly diagnosed than PE
- But mortality from PE twice that of DVT
- Anticoagulation is the preferred treatment for VTE
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter is an important therapeutic option in the management of selected patients with VTE – anticoagulation contraindicated, complications, or fails to protect.
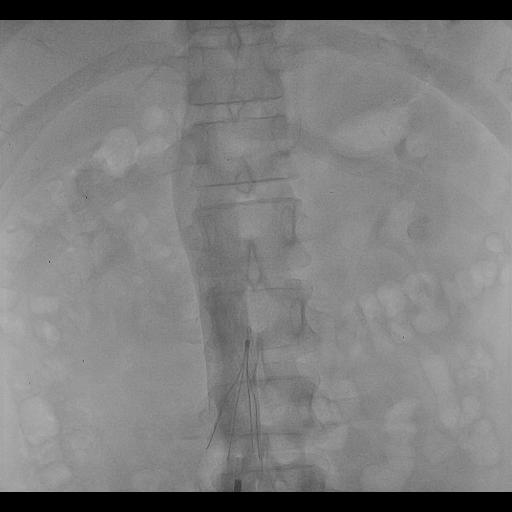
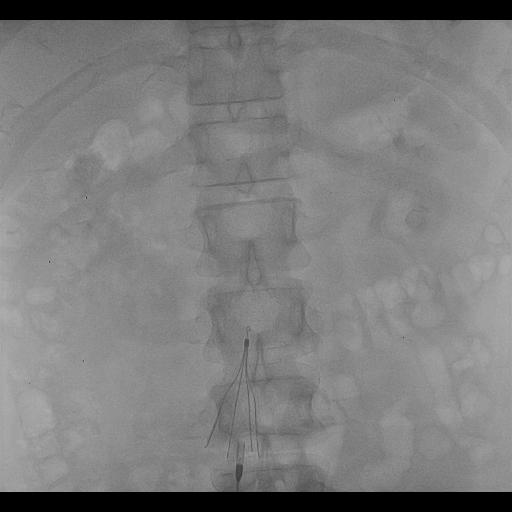
What are the types of IVC filters?
Permanent IVC filter:
- The Long-term need for mechanical prophylaxis against PE
- Absolute contraindications to anticoagulation
Temporary IVC filter:
- Temporary risk of PE
- Contraindication to anticoagulation resolved
What are the indications for IVC filter placement?
Classical indications:
- Absolute contraindication to anticoagulation
- A Complication of anticoagulation resulting in cessation of therapy
- Failure of anticoagulation
- Propagation/progression of DVT during therapeutic anticoagulation
Expanding Indications with DVT:
- Iliocaval DVT or large, free-floating proximal DVT
- Difficulty establishing therapeutic anticoagulation
- Massive PE treated with thrombolysis
- Chronic PE treated with thromboendarterectomy
- Thrombolysis for iliocaval DVT
- VTE with limited cardiopulmonary reserve
- Recurrent PE with a filter in place
- Poor compliance with anticoagulation
- High risk of complication of anticoagulation
Expanding indications without DVT:
- Trauma patient with a high risk of VTE
- A surgical procedure inpatient high risk for VTE
- Medical condition high risk of VTE
What are the risks of IVC filter placement?
- Bleeding manifestations
- Infection
- Allergic reaction to medications and dye used during the procedure
- Blood clots that travel through lungs
- Blood vessel damage at the insertion site
- Legs swelling due to blockage of blood vessel
- Respiratory related problems
- Death
What are the complications of IVC filter placement?
- Thrombosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Migration of IVC filter
- IVC perforation
- Filter fracture
How is IVC filter placement done?
Understanding the procedure
Before the procedure:
Dietary instructions:
Follow instructions by your doctor about hydration, which may include:
- Stop heavy meals or processed food before 8 hours of the procedure
- Stoplight meals before 6 hours
- Stop drinking milk or carbohydrate drink before 6 hours
- Stop drinking water or clear fruit juice before 2 hours
General instructions:
- List all the current medications and supplements used
- Any allergies towards the medications should be reported
- Stop aspirin and ibuprofen if you are taking previously because these can thin your blood. Do not take before the procedure
- Changing /stopping the regular medication, especially if the patient is diabetic
- Antibiotic is given to prevent infection
- Blood samples are taken for clinical investigations
- Vitals are checked
During the procedure:
- Small insertion is made in the neck or groin area
- The catheter will be inserted and directed towards inferior vena cava using X rays imaging (Contrast dye is inserted in a catheter to show IVC clearly)
- IVC filter is inserted through the catheter will be released, expanded and attached to IVC
- The catheter will be removed
- A bandage is placed over the catheterized area to stop bleeding and infection.
After the procedure:
- Vitals such as Blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, respiration rate, blood oxygen level will be monitored.
- You will be instructed to rest in the ICU for 24 hours.
- Patient hospital stay will be 2 to 4 days.
- If the catheter insertion is at the groin area, you may ask not to bend or cross your legs
- Infections and bleeding manifestations are checked at the insertion site
- You will be instructed to keep hydrated that will help you in washing off the contrast dye
- Blood tests, Chest X-ray and Electrocardiogram(ECG), Echocardiogram will be done
What is the uniqueness of IVC filter placement by Dr C Raghu?
Our Specialities
- Conditions
Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis
Diagnosis
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT

Dr. RAGHU
MD, DM, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
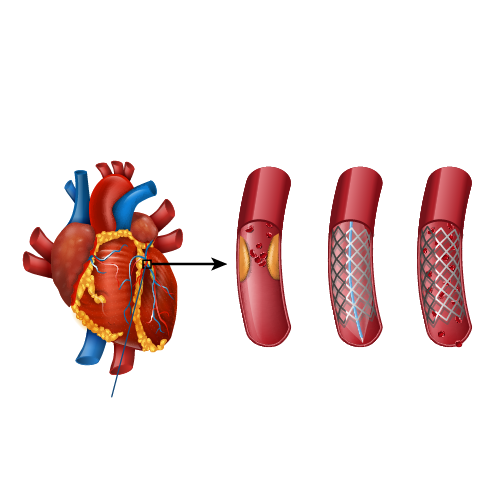
Angioplasty
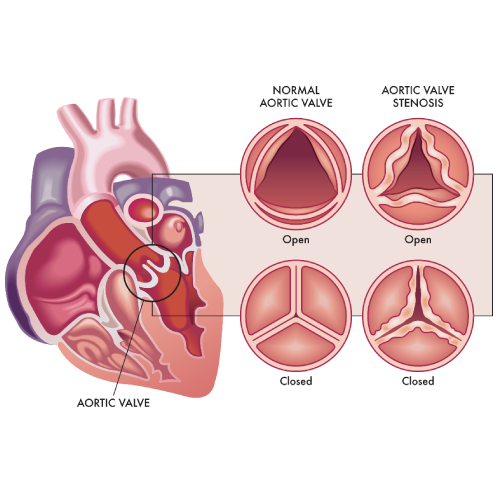
Aortic Stenosis
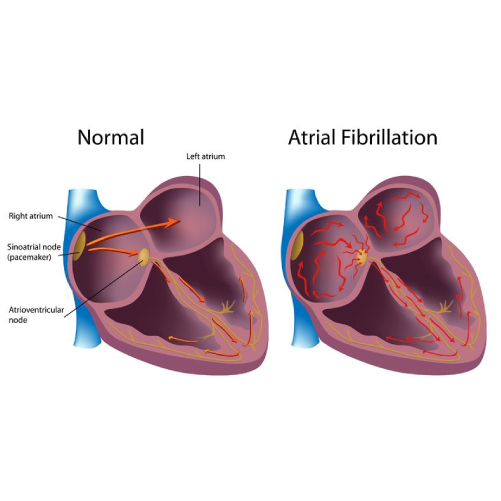
Atrial Fibrillation