Diagnosing Congestive Heart Failure
There are many scenarios where you might want to see a doctor and find out whether you’ve developed heart failure. Perhaps you have a history of heart disease in the family and would like to assess your risk levels.
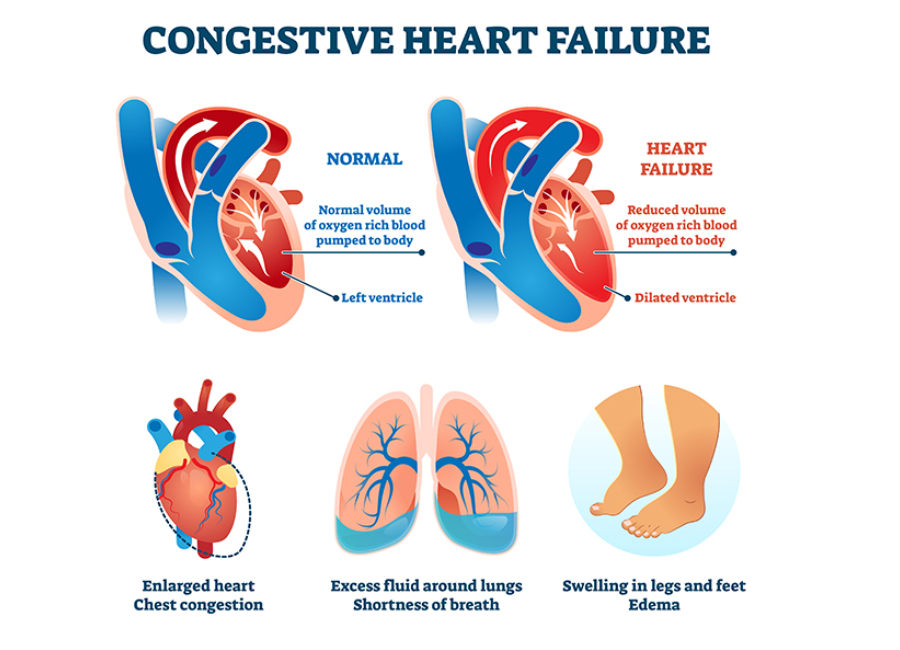
Or you might have developed symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and swollen feet, that are indicative of heart failure. (Check out our previous article for a detailed glimpse of heart failure symptoms.)

Or you might have completed an initial round of investigation and want a closer look at the root cause of heart failure. In any case, it’s essential to have a fair idea of the steps involved in diagnosing heart failure. Let’s take a look.
Family History and Medical Background
Diagnostic efforts for heart failure serve two primary purposes :
- To determine the underlying cause
- To assess the extent of the heart’s malfunction
The first thing a doctor will do is get a complete picture of your medical history. They’ll want to know the details of any symptoms you might have been experiencing. Also, they’ll ask about your diet and lifestyle, including your habits pertaining to exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Additionally, they’ll ask one or more of the following questions:
- Do you have pre-existing conditions like high cholesterol levels, hypertension, diabetes, etc.?
- Have you undergone treatments like chemotherapy?
- Do you have a family history of cardiovascular diseases?
Your answers to these questions will give your doctor a better idea of your current physical condition.
Physical Examination
Next, the doctor will perform a thorough physical exam to analyze your heart activity. They’ll likely start by calculating your BMI and body fat percentage. Also, they’ll measure your vitals, including blood pressure and heart rate.
Additionally, they might use a stethoscope to identify abnormal heart sounds or murmurs that indicate a faulty heart valve. They’ll also watch out for soft noises or bruits to identify the narrowing of arteries.
They’ll examine your skin to see if it feels cold or looks discolored. They’ll also check your feet and abdomen for signs of fluid buildup. By the end of the physical exam, the doctor will have a better idea of your cardiovascular health.
Related : High Blood Pressure – Symptoms & Treatment
Diagnostic Tests
While a physical exam can indicate abnormal heart function, your doctor will likely run a few diagnostic tests to confirm the underlying cause of heart failure.
The most common tests include:
- Blood tests, such as complete blood count, lipid panel, liver and kidney function tests, and a fasting glucose test
- Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) test to determine the risk of hospitalization and death due to heart failure
- Chest X-ray to detect enlarged heart muscle or fluid buildup around the heart
- 12-lead ECG to monitor the heart’s electrical activity and identify signs of a heart attack or irregular heartbeat
- Echocardiography for a closer look at the heart’s chambers and pumping action in real time
- Coronary angiography to identify coronary artery disease
Other tests like radionuclide ventriculography, exercise testing, and endomyocardial biopsy may also be prescribed.
Related : What is Coronary Angiogram?
In Conclusion
Diagnosing heart failure involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and non-invasive procedures like X-rays and ECG. The key is to identify the underlying cause of heart failure, so that your doctor can decide the right course of treatment.
Dr. C Raghu is an experienced cardiologist who specializes in interventional cardiology. If you or anyone you know is at risk of developing heart failure, reach out to Dr. Raghu for a thorough diagnosis.
Book Online Consultaion
Diagnosing Congestive Heart Failure Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
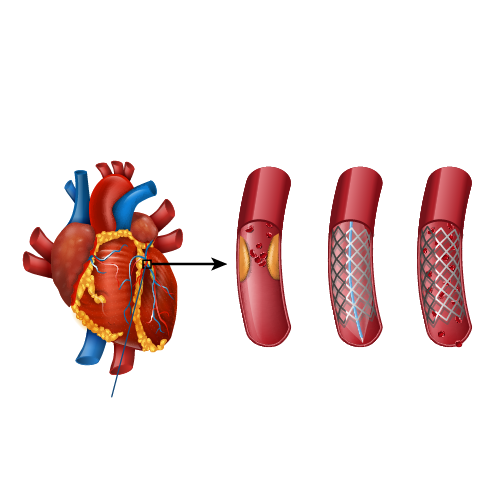
Angioplasty
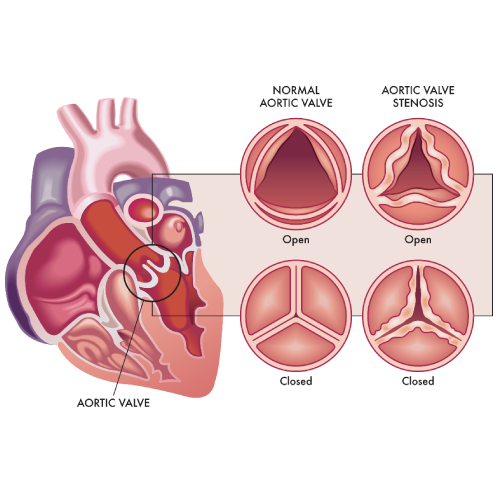
Aortic Stenosis
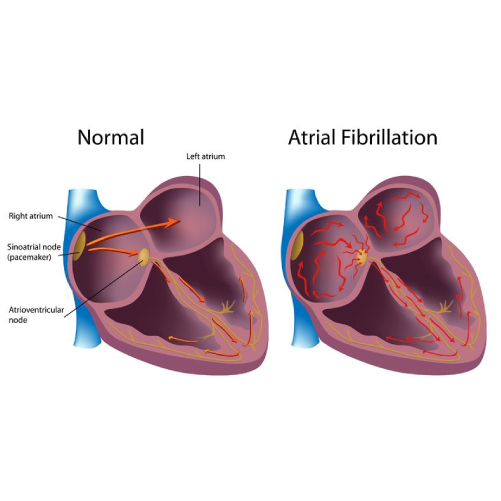
Atrial Fibrillation