High Triglycerides


Approximately 33 percent of American adults have high triglycerides or fats in the blood. It often goes undetected. Scientists believe that having high triglyceride levels can result in stroke and heart attacks. This risk is higher in people with type 2 diabetes and lower good HDL levels. So, those in the danger zone should also get their triglyceride levels tested. It is not a life-altering condition but demands some strict lifestyle changes with medications.
Read to learn more about high triglycerides.
What is It?
Triglycerides high means your blood has fats in high numbers. Your bodies get triglycerides from foods containing oils and butter. Moreover, when you eat more calories than required, your body converts these into triglycerides for easy access whenever your body needs energy. Hence, they are vital fats that give you energy. However, high levels exacerbate your risk of developing heart disease. But what is the triglycerides normal range? Let us discuss.
Triglycerides Levels
A lipid blood test helps you know your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. It can be a fasting (no eating for 9-12 hours) or a non-fasting test. Be sure of the nature of the test in advance.
Broadly, the levels for the triglycerides test on an empty stomach are as follows:
- Normal Range: Below 150 mg/dL
- Borderline: Between 150 and 199 mg/dL
- High: Between 200 and 499 mg/dL
- Very High: 500 mg/dL and above
Doctors recommend people over 20 to monitor their triglycerides and cholesterol levels routinely. The ideal frequency depends on your cardiovascular risk factors and age. However, adults must undergo the test every four to six years.
Symptoms
Typically, people experience no high triglycerides symptoms. However, those with extreme hyperglyceridemia develop xanthomas, bumps on the skin that develop when lipids accumulate under the skin. They appear around your eyelids, but may also form on the palms, elbows, or knees.
Causes
High triglycerides causesinclude the following:
- Genetic lipid disorders
- Medications
- Underlying medical conditions
- Lifestyle factors
Genetic lipid disorders
These affect cholesterol and triglycerides. Common disorders include:
- Familial hypertriglyceridemia: High triglycerides
- Familial combined hyperlipidemia: Low HDL or high LDL cholesterol and high triglycerides
- Familial chylomicronemia syndrome: Triglyceride levels over 1,000 mg/dL.
- Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia: High total cholesterol and high triglycerides
Medications
Your ongoing medicines also put you at a high triglycerides risk. These include:
- Oral estrogen
- 2nd generation antipsychotic drugs like olanzapine and clozapine
- Beta-blockers
- Corticosteroids
- Tamoxifen
- Cyclophosphamide
- Antiretroviral (ART) protease inhibitors for HIV treatment
- Thiazides
When medications increase triglycerides levels, your doctor will help you recommend a competent solution, such as switching to an alternate medicine or changing the dosage. But speak to your doctor and do not act on your own.
Medical Conditions
Some underlying medical conditions also spike your triglycerides levels. These are as follows:
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Insulin resistance
- Hypothyroidism
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Metabolic syndrome
Females and those assigned females at birth have other risk factors. These are:
- Pregnancy (mainly in the third trimester)
- Menopause
Lifestyle Factors
Your lifestyle can increase or decrease your triglycerides levels. Normally, people who consume excessive alcohol are at risk. Further, those who eat fatty foods and sugar may also have higher than normal levels.
Some factors that aggravate your risk are:
- Excessive drinking
- Heating high levels of refined carbs and saturated fat
- Leading a sedentary life
Treatment
Lifestyle Changes
Often the first line of high triglycerides treatment involves lifestyle changes.
Some suggestions are:
- Shed some kilos: If you are obese or overweight, consider losing a few kgs and maintaining an ideal body weight.
- Look for better fats: Not all fats are bad. So, be careful of the fats you eat. Reduce trans fats and unhealthy fats from your diet. Instead, opt for polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. Studies suggest that Omega-3s present in fatty fish are beneficial. They lower triglycerides. While healthy, all fats have a high calorie count. So, please eat them in moderation.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Even smaller quantities of alcohol can increase triglycerides levels. So, curtail yourself to one drink a day.
- Be physically active: Exercise can significantly impact the triglyceride levels. Even a thirty-minute workout for five days a week will help.
Medication
Those with high triglycerides and heart diseases will require medications to lower their levels. Some commonly recommended treatments include:
- Niacin or Nicotinic Acid: It lowers the levels by up to 50 percent.
- Fish Oil with Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These help maintain your triglycerides levels. Flaxseeds and chia seeds are good plant sources for Omega-3. But you can also get fish oil supplements.
- Fibrates: They help lower triglycerides and cholesterol levels
Tip: Disclose all your ongoing medications with your healthcare professional. Sometimes, they are the underlying cause of a rise in triglycerides.
To Sum Up
In triglycerides and cholesterol, the most crucial thing is undergoing regular screenings. So, please do not avoid routine check-ups. Basis your current levels, your doctor will alter the treatment plan. Generally, medication and lifestyle changes are beneficial for all.
Dr. Raghu is a reputed cardiologist. He is popular for his invaluable contributions and has served thousands of people to live better. So, contact Dr. Raghu if you ever need a good cardiologist in Hyderabad. He will help you with the best practices to keep your triglycerides in check.

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
Angioplasty
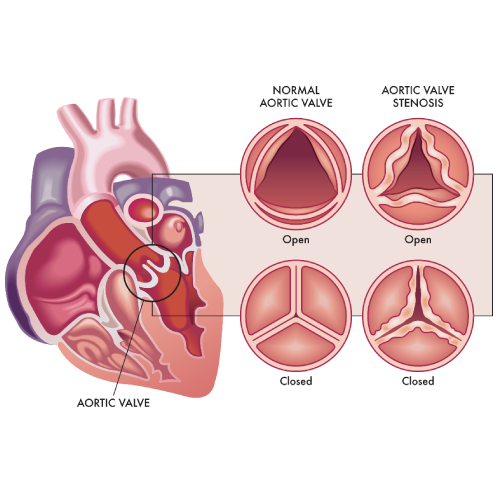
Aortic Stenosis
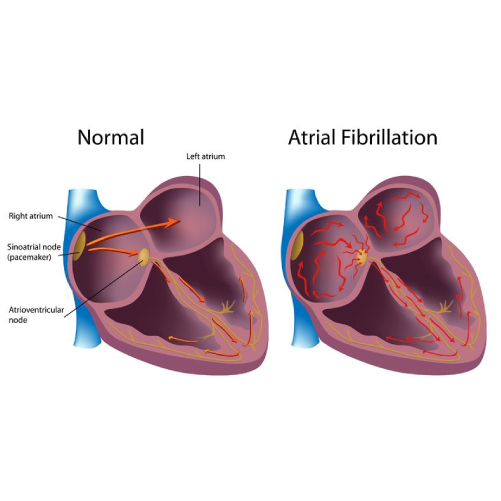
Atrial Fibrillation