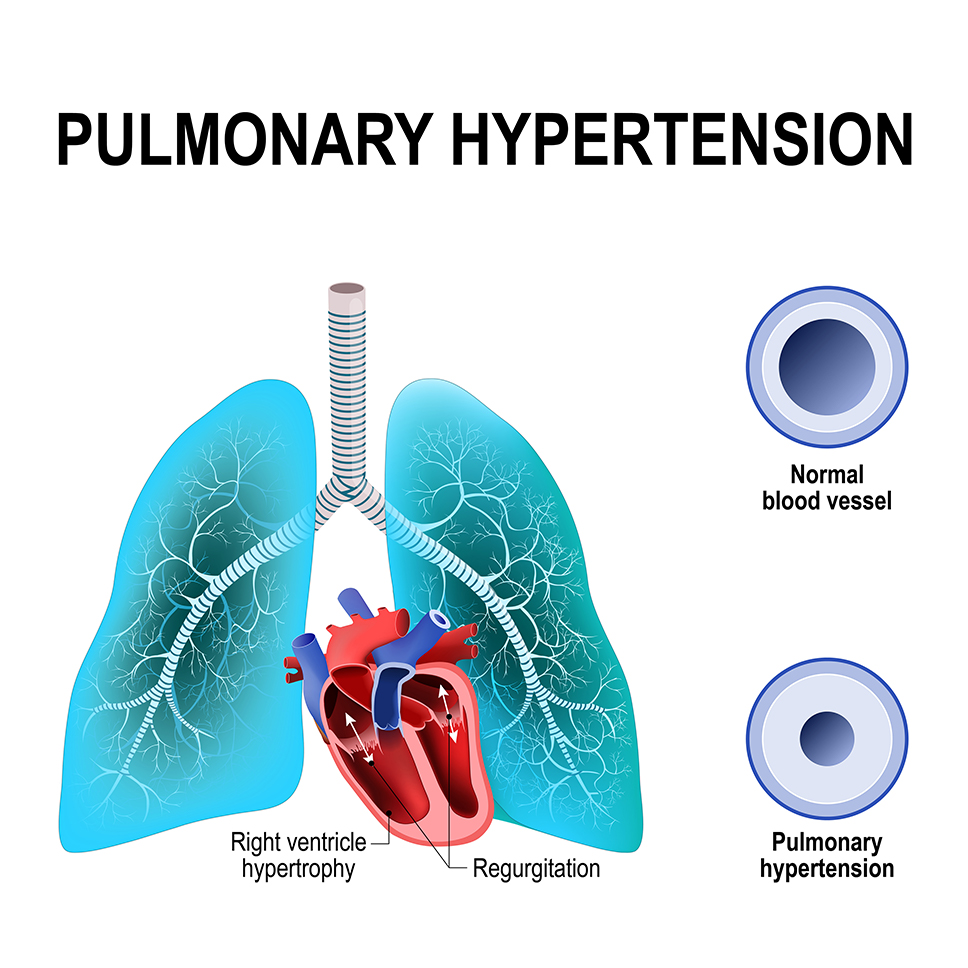
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) is a rare form of pulmonary hypertension that occurs when blood clots, or thrombi, form in the arteries of the lungs and do not fully dissolve.
dr raghu | Dr Raghu - Page 2
Regular consumption of artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose can have an adverse effect on your heart. They increase your risk of coronary heart disease, strokes, and other ailments.
Aspirin is one of the most widely used over-the-counter drugs in the world. It comes in several forms, but the most common way to take it is as a pill. It belongs to a specific class of medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Many people have heart disease, but not all of them know it. Doctors use a variety of tests to identify cardiac ailments and their underlying causes. Coronary angiography is one of the most common diagnostic tests that doctors use.
While it’s considered a safe and minimally invasive procedure, coronary angiography comes with a few risks. You can read more about the potential risks and complications in our previous blog.
The good news is that you can avoid side effects with proper care after the procedure. If you’ve recently had coronary angiography or are going through one soon, here is what you need to do after the procedure:
Avoid Heavy Physical Activity
It’s important to rest after coronary angiography. Avoid lifting heavy objects or resuming your exercise routine right after the procedure. Make sure you get plenty of sleep and let your body and mind relax for at least a week after angiography. Ask your doctor if you’re unsure when to hit the gym or start exercising.
Embrace Healthy Habits
Avoid cigarettes for at least a few days if you are a smoker. Smoking can cause spasms in the coronary arteries, leading to a heart attack or stroke after your angiography. Also, avoid alcohol consumption, and make sure you eat a balanced diet.
If you are a coffee drinker or have high blood pressure, avoiding all caffeine products (coffee, tea) and salt for several days following your procedure may be a good idea. The most important thing is to listen carefully to what your doctor tells you about caring after coronary angiography to avoid any other complications during recovery or later down the road.
Be Careful About Removing the Bandage
A crucial step to caring after coronary angiography is to avoid removing the bandage until the morning of the second day after the procedure. Also, you should not remove it yourself. Let someone else help you remove it. You must consult your doctor or nurse before removing the bandage.
Expect Soreness and Pain for a Few Days
Your arm or leg (where the catheter was inserted) might feel sore for a few days following a coronary angiogram. The discomfort you feel is usually caused by the catheter or dye used for the test.
The catheter may have been left in place too long, leading to irritation and inflammation. Or it could be a reaction to the dye that was used to take images of your arteries during the procedure. It can also happen if you’re allergic to any component of either one.
In most cases, the pain and soreness should subside after a few days. If the pain persists or the arm/leg becomes numb, it’s a good idea to reach out to your doctor. Also, if you have a fever or trouble breathing, call your doctor right away.
If you are bleeding from the incision site, apply direct pressure with a gauze dressing until the bleeding stops. Don’t remove the dressing unless instructed by medical staff at the hospital.
Conclusion
Coronary angiography is a safe and effective procedure that can give you a better understanding of your heart health. If you follow your doctor’s instructions, you’ll be on the road to recovery in no time.
Dr. C Raghu is a renowned cardiologist who has treated thousands of patients with cardiac ailments. If you have any concerns or questions about coronary angiography, feel free to reach out to Dr. Raghu today.
Book Online Consultaion
Care After Coronary Angiography – Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
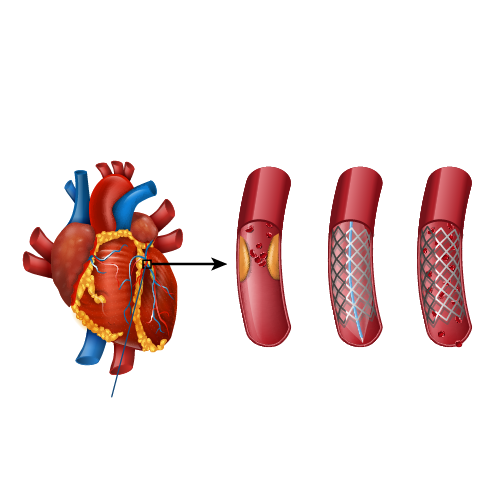
Angioplasty
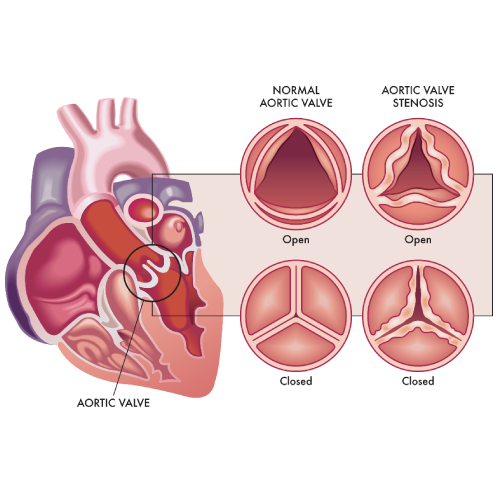
Aortic Stenosis
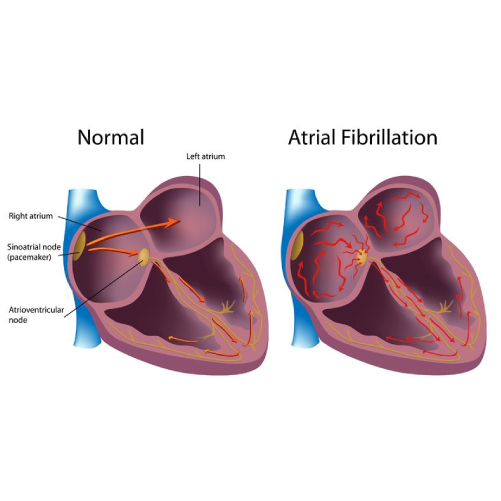
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Septal Defect
Heart is a complex organ and can get affected by diseases that can affect various systems of the heart. The common heart ailments that would be observed include:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) – accumulation of cholesterol plaques within the walls of the blood vessels (coronary arteries) supplying the heart. This leads to obstruction to blood flow of the heart that can cause chest pain or heart attack.
Valvular heart disease: Heart valves are flap-like structures akin to doors between rooms. They control the blood flow between various chambers of the heart. They play a key role in blood circulation.
There are four valves in the heart
- mitral and aortic valves on the left side of the heart
- tricuspid and pulmonary valves on the right.
These valves can either get narrowed (stenosis) or get “leaky” (regurgitation).
Cardiomyopathy: This disease affects the heart muscle leading to inefficient heart pumping efficiency. Cardiomyopathy can be either due to:
- Direct heart muscle diseases – Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy.
- Indirect heart muscle diseases –
- Consequent to
- heart attack (ischemic cardiomyopathy)
- infective (myocarditis) and
- heart rhythm problems
- Consequent to
- Heart Rhythm problems (Arrhythmias)- Normal heart rate is between 50-100 beats per minute. The maintenance of heart rhythm within a specific range is possible due to an efficient electrical system of the heart also called the conduction system.
- Slow heart rate – Bradycardia usually due to retardation of conduction within the conduction system of the heart. The most common cause is due to age related degeneration of the conduction system. The garden variety disease causing slow heart rate is called complete heart block.
- Fast heart rate – Tachycardia in this disease there is an accelerated conduction of electrical impulses – if the fast heart arises in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) it is called ventricular tachycardia if it arises in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart it is called supraventricular tachycardia.
Doctors usually recommend a battery of tests based on the system of the heart that has been affected. Based on a detailed history followed by a detailed physical examination, appropriate battery of tests would be suggested. The diagnosis of the heart ailment is critically dependent on the results of tests.
In addition to confirming the diagnosis, test results might indicate the disease complications and thus your doctor is able to stage the disease and the possible outcomes.
Related : Basics about Heart Failure
Blood tests:
- Complete blood count (CBC): A complete blood count helps to detect infection, anaemia and other blood disorders. Anaemia is a common finding in heart failure, plus it also contributes to worsening of heart failure. A low platelet count may be caused by medications such as diuretics or heparin.
- Cardiac troponins (cTn1, cTnT, high sensitivity troponins): It is an important blood biomarker useful for the detection and predicting outcomes of chest pain or heart attack. Cardiac troponins may also be high in other heart related conditions like acute myocarditis, coronary vasospasm and non-cardiac conditions (e.g. sepsis, chronic kidney disease).
- Electrolytes, urea and creatinine: Assessment of kidney function is essential in all cardiac patients. Both kidney and cardiac disease share the same risk factors and either disease can lead to poor outcomes of the other disease. In addition, cardiac drugs’ doses need to be modified considering the kidney function.
- Liver function tests:: Certain drugs such as statins and amiodarone, which are commonly prescribed for patients with heart disease, can trigger liver failure. Liver failure could also be a consequence of heart failure.
- Thyroid function test: Medication for heart disease like amiodarone may cause hyper or hypo thyroidism. Altered thyroid hormone can also cause heart dysfunction and responsible for coronary artery disease.
- Brain Natriuretic Peptides (BNP or N-terminal pro BNP): BNP is a useful tool to differentiate between cardiac and non-cardiac causes of shortness of breath. High levels of BNP and N terminal pro BNP is associated with increased severity of heart disease and greater risk of hospitalization.
Related: Types of Heart Failure
Electrocardiography(ECG):
This test detects and records the electrical activity of the heart. This is a simple, non-invasive test which is very useful to determine abnormalities in the heart rate, rhythm and to identify risk of damaged heart muscle or other structural changes in the heart. This test detects the presence of arrhythmias and coronary artery disease.
Exercise stress testing:
Exercise makes your heart work harder. Exercise stress testing is done either on a treadmill or cycle ergometry with the patient connected to an electrocardiogram. Exercise stress testing may identify myocardial ischaemia, haemodynamic/ electrical instability, or other exertion-related signs or symptoms. When an individual is not able to exercise, medications are given to stress the heart and the response is evaluated.
Chest X-ray:
Chest X ray is very useful to differentiate whether shortness of breath is due to a respiratory disease or heart disease. It can also help in detecting complications of heart failure such as cardiomegaly, interstitial oedema, pulmonary oedema and pleural effusions.
Coronary angiography:
Coronary angiography is useful to determine the health of the coronary arteries. In this test, a catheter is inserted into the coronary arteries and a dye is injected to produce clear X ray images of the coronary arteries. This helps to find out the presence, location and extent of vessel narrowing. The results also help to decide which type of treatment would be most appropriate for correction of heart problem.
Echocardiography:
This test gives an ultrasound image of the heart. Echocardiography can provide information about the size and shape of heart chambers, blood flow velocities, heart muscle function when they contract and relax, abnormalities of the movement of the heart wall, valve function, and presence of thrombus (blood clot) in the heart.
Stress echocardiography helps in detecting decreased blood flow to heart during exertion. In this test, echocardiography is done immediately post stress. The stress can be exercise or could be induced by medications.
Myocardial perfusion scanning (MPS):
MPS is a non-invasive test which helps to determine how well blood flows through your heart muscles. In this test, a small amount of a radioactive substance is injected into the blood. The test evaluates the severity of coronary artery disease and provides guidance regarding the need as well as success of invasive procedures like angioplasty and stent insertion.
Cardiac Computerized Tomography (CT):
Cardiac CT provides detailed images of the heart. This helps to identify structural abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels such as aneurysms, valve dysfunction and damage to the pulmonary vasculature. Cardiac CT also provides information about patency of grafts following coronary artery bypass graft.
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Cardiac MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency to provide detailed 3D images of the heart and surrounding structures. The image provides accurate information about cardiac volumes, muscle mass, contractility, and how efficiently the heart is pumping. Like cardiac CT, cardiac MRI also helps to provide information about patency of grafts following coronary artery bypass graft.