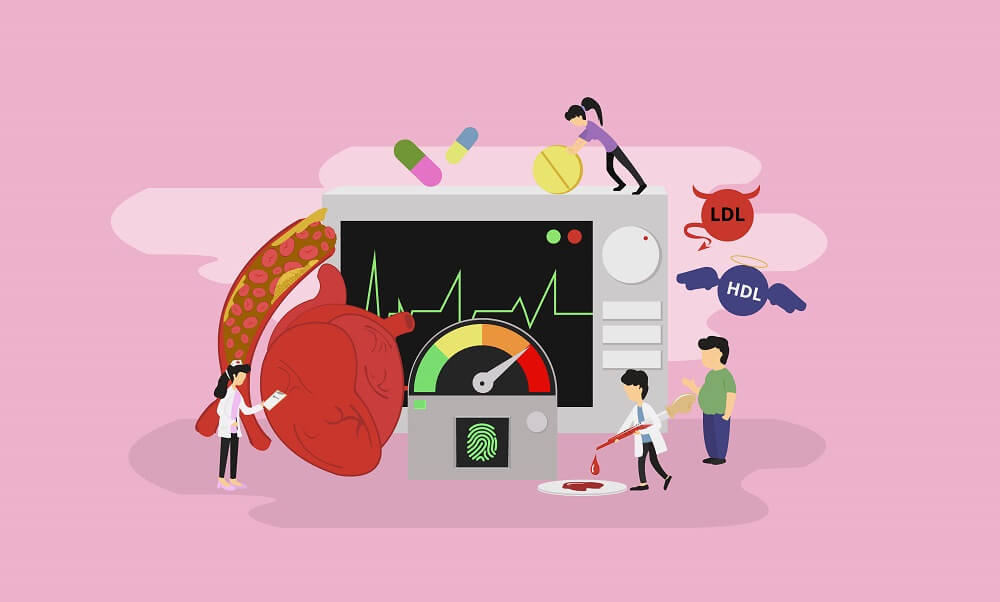
Cardiovascular diseases continue to be a leading cause of mortality globally, with calcified coronary arteries posing a significant challenge in interventional cardiology.
dr c raghu | Dr Raghu
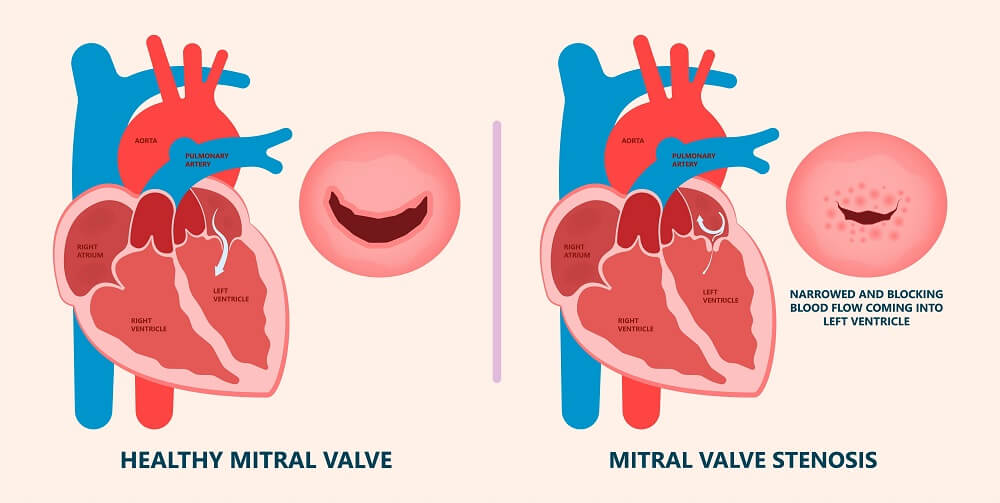
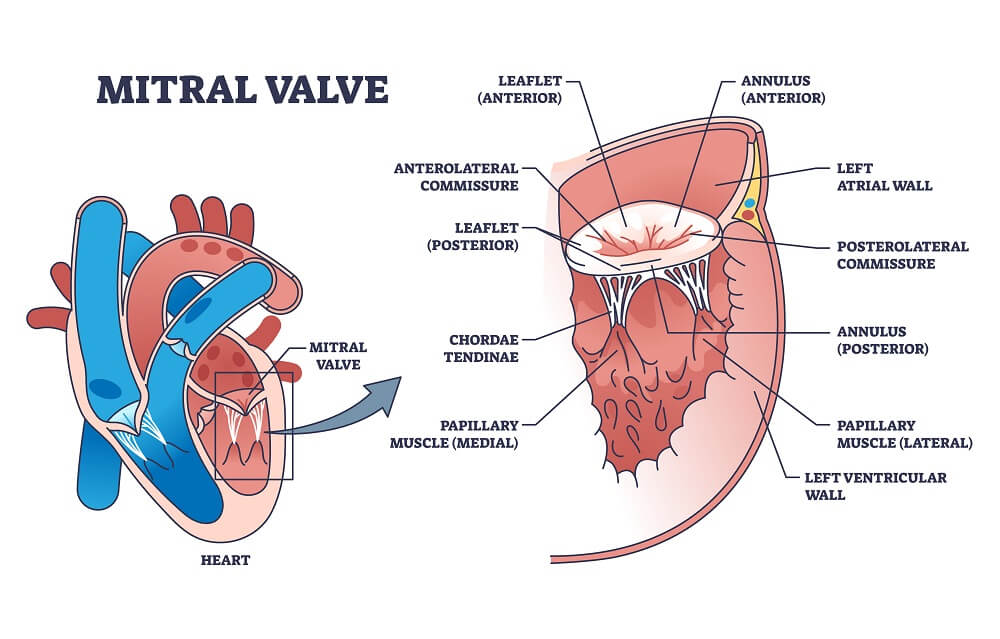
Mitral Valve is the one which is tucked between the upper left atrium and lower left ventricle and when it gets narrowed, this becomes a major heart health issue which is called Mitral Valve Stenosis.
Under this condition, the blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle is restricted and the blood starts to flow back into the left atrium, blood vessels of the lungs and to the right side of the heart too.
Though stenosis occurs, symptoms don’t appear for a major part of one’s life, say 8 to 10 years.
But in India, research suggests that the progression is quicker than in the rest of the world and symptoms surface within 8 to 10 years. As for the severity, such can be mild or severe.
What are the possible reasons for mitral valve stenosis that we know?
- Rheumatic fever can be a discrepancy due to streptococcus infection.
- Calcium reserves due to old age.
- The congenital shortcoming in the mitral valve.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus, can also contribute to this.
- Radiation therapy is done to the chest.
Notable Symptoms Of Mitral Valve Stenosis:
- Breath shortness.
- Heart murmurs.
III. Cough.
- Fatigue.
- Speedy Heartbeat (palpitation).
- Chest Pain.
VII. Swelling in leg, feet and ankles.
VIII. Heart rhythms get abnormal.
What are the difficulties that arise from Mitral Valve stenosis?
The following issues have come to light.
- Abnormal Heart Size:
This is called heart enlargement where the upper left chamber (left atrium) gets bigger in size and the right side of the heart which is due to pressure taking place as a fallout of mitral valve stenosis.
Upper chambers get stretched and get bigger and this often leads to strange heart rhythm.
- Formation of Blood Clots:
If we ignore abnormal or ultrafast heartbeats, we find blood clots in the left atrium. Further, such clots can split and travel to different parts of the body and this gives rise to troubling consequences like paralytic stroke.
Pressure increases in the upper left chamber and lungs and this gives rise to risky fluid accumulation which can also cause heart failure.
Blood pressure increases in the arteries which facilitate blood flow from the heart to the lungs (pulmonary arteries).
- Stroke:
- Endocarditis.
How do the doctors (the best cardiologist for valve replacement for that matter) diagnose mitral valve stenosis?
This is a complication which goes unnoticed for a few years but when the stenosis progression takes place, problems appear. Doctors prescribe the following tests to detect the disease.
- Physical examination and doctors look for heart murmurs.
- Electrocardiogram: To decipher the electrical activity in the heart.
- Echocardiogram: By focusing on ultrasound images, heart chambers are checked alongside the valves and blood vessels.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram: In this test, doctors locate the cause and severity of the stenosis.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Before doing the mitral valve replacement surgery, coronary angiography is done and this is a procedure which is exclusively recommended for those above 40 years of age.
- Chest X-rays.
Dr C Raghu: The Saviour Of Heart Health.
If left untreated and ignored, the small problem can grow into a big problem (and would need more money for treatment).
Smashing the boundaries, his clinic embraces cutting-edge technology and such machines help in effective and world-class treatment of a range of heart issues, at a reasonable price but still, one has to remember that no cost is high for saving a life and to lead a healthy life.
As a result, Dr C Ragu’s clinic is the shining jewel of Hyderabad city as the eclectic world of Dr C Raghu’s modern cardiology enthralls everyone.
We make a successful pitch for supreme heartcare and treatment excellence in India which is at par with the developed world located in the west and is more affordable too.
Truly, Dr C Raghu is widely regarded as the best cardiologist for valve replacement and has a large fan following across the world.
Book Online Consultaion
How Cholesterol Is Linked to Heart Disease Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
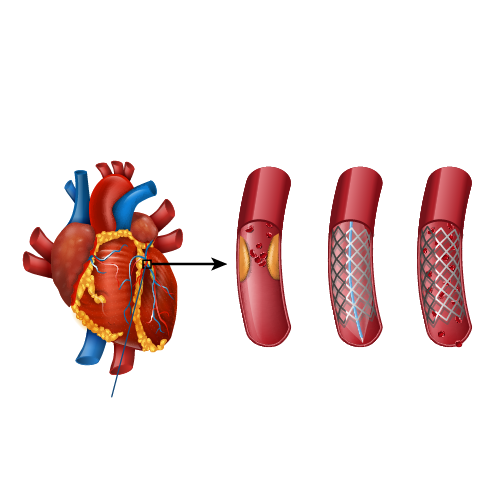
Angioplasty
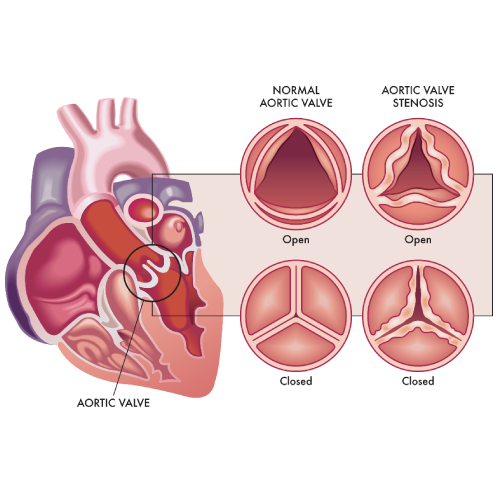
Aortic Stenosis
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Septal Defect

Heart disease, once considered primarily an ailment that affected people in their 60s or 70s, is now becoming a significant concern in children. According to a report in the Times of India, there has been a disturbing increase in the number of children suffering from heart diseases and, tragically, even losing their lives to these conditions.
In this article, we will delve deeper into heart disease risk in kids and discuss a few useful tips to prevent a heart attack and other cardiovascular conditions from a young age.
The Rising Prevalence of Heart Disease in Children
Heart disease is increasingly becoming a significant health issue among children worldwide. While congenital heart defects have been recognized for years, there is a concerning rise in acquired heart diseases in children, including cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, and atherosclerosis.
Additionally, there have been several reports of individuals in their 20s and 30s succumbing to heart attacks. That, in turn, emphasizes the need to identify and address heart disease risk in young people. The sooner we parents recognize these risks and inculcate heart-healthy habits in their children, the lower their risk of developing chronic cardiac conditions.
Contributing Factors to Heart Disease Risk in Kids
In this section, we will take a closer look at a few factors that are increasing heart disease risk in kids.
Unhealthy Diet
The modern lifestyle has led to a surge in the consumption of processed and high-calorie foods, leading to childhood obesity and related cardiovascular issues. Such diets are low in essential nutrients and high in unhealthy fats and sugars, contributing to elevated cholesterol levels and other heart disease risk factors in kids. Childhood obesity can also make children more vulnerable to metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes.
Sedentary Lifestyle
With the advent of technology, children are spending more time on screens and less time engaging in physical activities. This sedentary lifestyle has adverse effects on their cardiovascular health, leading to weakened heart muscles and poor circulation.
Genetics and Family History
Family history plays a crucial role in determining a child’s susceptibility to heart disease. If there is a history of heart problems in the family, the child may be at a higher risk. Several studies also suggest that prenatal factors, such as maternal nutrition during pregnancy, smoking, or exposure to environmental toxins, can influence the child’s heart health in later life.
Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress and mental health issues have been associated with heart disease risk in kids. Stress can trigger unhealthy coping mechanisms like emotional eating and contribute to high blood pressure and inflammation.
Identifying Early Warning Signs
Heart disease in children may present differently than in adults, making it essential for parents and healthcare providers to be vigilant about early warning signs. Common symptoms that could indicate a heart problem in children include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fainting spells.
Routine health check-ups play a critical role in identifying potential heart issues in children. Through regular examinations and tests, healthcare professionals can spot risk factors early and offer appropriate interventions.
Preventive Measures and Management
While heart disease is becoming more prevalent in kids, there are ways to minimize its risk. Here are a few tips to prevent a heart attack and other conditions in children:
Promoting a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
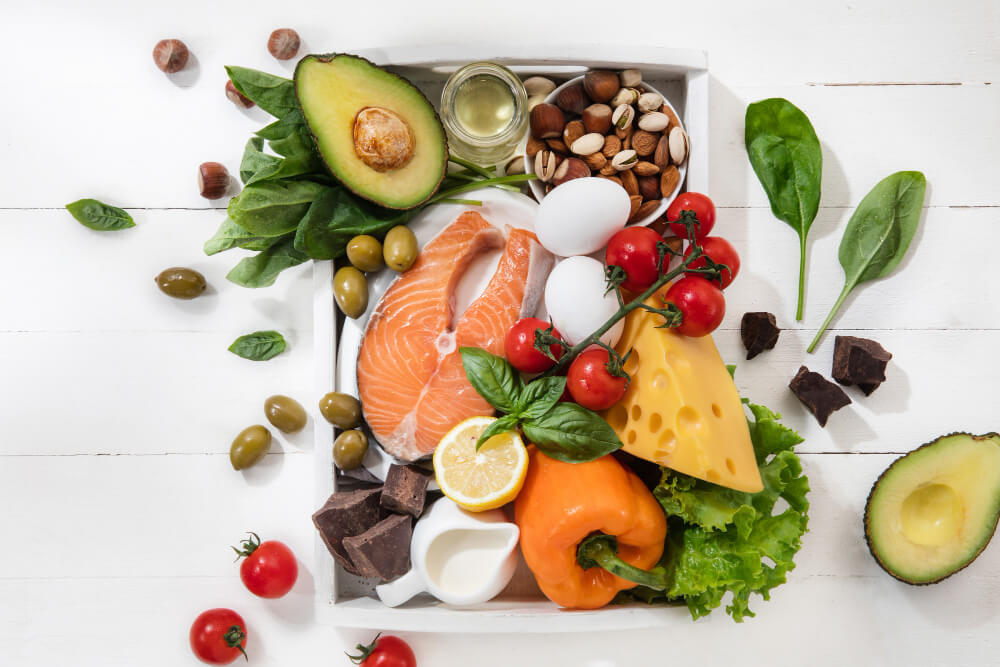
Prevention is always better than cure, and instilling heart-healthy habits in children is the first step toward reducing heart disease risk. Start by encouraging your child to be more active. Regular physical activity is crucial not only for maintaining a healthy weight but also for strengthening the cardiovascular system. Nutrition also plays a vital role in preventing heart disease in children. Incorporating more heart healthy foods like nuts, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your kid’s diet is crucial.
Final Thoughts
The rising incidence of heart disease risk in kids is a concerning global health issue. Understanding the contributing factors and implementing preventive measures are crucial steps in addressing this problem effectively. By promoting healthy lifestyles, conducting regular health check-ups, and raising awareness among parents, healthcare providers, and communities, we can work towards safeguarding the heart health of the younger generation. Together, we can ensure a healthier future for our children.
Dr. C Raghu is an eminent interventional cardiologist who is often regarded as the best heart specialist in Hyderabad. If your child has been diagnosed with a heart condition, reach out to Dr. Raghu today to discuss the right treatment options.
Book Online Consultaion
Heart Disease Risk In Children: Understanding The Growing Concern
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases

Angioplasty

Aortic Stenosis

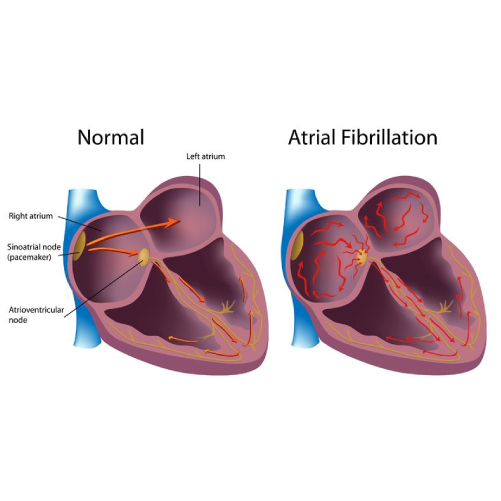
Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial Septal Defect

Hyderabad, July 9 (IANS) Vitamin D deficiency is not a major risk factor for heart attacks or atrial fibrillation. It is a soft target and not a hard point in management of heart disease, opines leading cardiologist Dr C. Raghu. According to him, the major risk factors for heart attacks remain hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol and family history
In an interview with IANS, the senior interventional cardiologist and clinical director at Yashoda Hospitals, Secunderabad, explained some of the recent advances in the domain of heart heath.
Q: How do you look at the recent study that Vitamin D might reduce the risk of heart attacks and prevent irregular heartbeats?
A: These are not therapies for these problems. These are in addition to what all other measures a person takes. People might think that Vitamin D is the only thing. Heart disease is a multi-factor disorder.
Still, the standard risk factors remain diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol and family. These have strong correlation. Vitamin D to treat or to prevent heart attack is still a long term goal even going by this study.
Many studies might come on various factors and they might choose positive benefits but for these positive benefits to translate to clinical medicine is a long process.
There are many medications which can definitely reduce the heart event rate but for this many factors have to be addressed properly.
Vitamin D is a very soft target not a hard point. It is not the only thing. People should not think that if I take Vitamin D, I will be okay. I think fundamentals remain the same.
Diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol and physical activity continue to remain major pillars. These risk factors have to be addressed to prevent heart attack.
Q: How common is atrial fibrillation in the Indian context?
A: Atrial fibrillation is worsening like heart disease. It is a multifactorial disease. Most of the patients of atrial fibrillation are elderly women they have underlying hypertension, diabetes and they have stiff heart syndrome. In this group of patients prone to develop atrial fibrillation there are many hard end points which we can address rather than focusing on Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is not a major risk factor. In the Indian context also, atrial fibrillation is an emerging epidemic.
The main reasons are still uncontrolled high blood pressure, aging process and stiff heart. These will continue to be the main promoters of development atrial fibrillation. As a doctor, I would prefer to treat them rather than treat a very soft end point like Vitamin D.
Q: Will the use of higher doses of Vitamin D for a longer period negatively impact patients? If yes, what are the risks?
A: Yes. That is one of the major reasons why one should be very careful. Somebody might think what is the harm in consuming Vitamin D as it is a simple medication but that’s not the way. Unsupervised Vitamin D use for a prolonged period of time can lead to lot of medical complications.
Some people might develop renal dysfunction, some people might develop hyperparathyroidism or produce more calcium (hypercalcemia). There are a lot of metabolic problems that may happen if somebody takes long duration vitamin D without proper medical supervision.
Presence of deficiency of Vitamin D and its correction are not the same. Sometimes correction of vitamin D deficiency might not reduce the primary problem. Prolonged consumption of Vitamin D and unsupervised especially elderly people tend to develop more complications.
One should be cautious in taking Vitamin D without supervision. Having said that, there are a lot of natural sources for production of Vitamin D. I would prefer my patients to have a natural way to produce Vitamin D by their body as a medication.
I encourage my patients to have 15 minutes of sunlight at least 2-3 times a week and at least once a week, do traditional remedies like application of castor oil to promote internal development of Vitamin D. These are simple measures one can take and naturally produce Vitamin much more quantitatively better.
Q-What are the other new or recent discoveries for managing heart health?
A: In the management of heart health, what the recent advances suggest is to stick to the traditional risk factors only. We now have a lot of objective data.
Let us consider Lipid. We have a lot of data which emerged in the last one decade indicating that people should target their Lipid. There is a lot of misinformation and misconception which are being propelled by various sources indicating that one should not believe in Lipid but we have strong data on the management of Lipid.
We have clear-cut numbers. What is LDL cholesterol a person should have. The numbers are different for a person who does not have heart attack and the one who had heart attack.
For a person who does not have a heart attack but has only Diabetes, we aim for LDL of less than 70. Same for a person with heart attack we aim for LDL cholesterol of less than 55. Same for a person who has got a high risk we aim for less than 35.
Previously we never used to aim for such low levels of LDL cholesterol. Now we understand that a very low level of LDL cholesterol will reduce the risk of having a cardiac event. This is one of the important advances which I think people have to be aware of.
There are different cut-off levels. When people go to a laboratory, the normal value of cholesterol creates confusion.
They will try to remain at a much higher level than what is desired for them. A lot of personalised medicine is coming for different subsections of people. It might look very less interesting for people but it is a very important and also inexpensive way to reduce the risk of heart attack.
One of the common ways to reduce heart attacks is to use aspirin. We all think that taking aspirin a day reduces the risk. Now with the availability of new data, we can understand that certain groups of patients get benefited and certain groups of patients can get harmed.
What we understand is that aspirin used for patients less than 60 who have diabetes and hypertension, they get better whereas for patients who are more than 60 years, we have to select patients who are going to be benefited rather than using aspirin for all of them as a blanket.
Aspirin therapy is very useful for prevention of heart stroke in people who already had a heart attack but for those people who never had a heart attack in the past or who never had bypass surgery, it is better to limit the use of aspirin among people who are less than 60.
So we have to differentiate between those who had heart attack angioplasty vis-a-vis those who never had an event and use aspirin selectively for people who already had heart attack and for those who did not have heart attack, we need to calculate the risk and then only use benefit of the therapy.
We now understand that women tend to have a higher risk of heart attack than what we were thinking in the past. Now a days, we see a lot of women also developing heart attacks. That is due to multiple to new risk factors which we were hitherto not knowing.
These risk are enhancers: for women who tend to premature menopause naturally or surgically, they will have a higher risk of heart attack. Premature means less than 40.
Women who have immunological disorders like Rheumatoid arthritis or SLE tend to have higher chances of heart attack. Such women possibly take aspirin to prevent heart attack.
In addition to traditional risk factors, we have risk enhancing factors for women and people who have South Asian ancestry like Indians. They play an important role for the development of heart attacks.
South Asian ancestry people tend to have higher risk of heart attack especially those with a family history of heart attacks in less than 50 years of age. Those people are at higher risk of developing heart attacks. That is also considered a risk enhancer.
That’s why you see a lot of young people developing heart attacks among the Indian population because of our propensity. It is not considered as risk factor but considered risk enhancer
Compared to the past we are seeing more and more women developing heart attacks at younger age. Previously we were not seeing this. Women who tend to have higher blood pressure during pregnancy may develop heart attacks. This is also considered a risk enhancer for a heart attack.
Q: Is building more data helping understand the risk factors and risk enhances better?
A: We continue to get data. The larger the data set, better we can understand the association.
Risk scores have also been developed. These risk scores help us to estimate what is the risk of a particular person to a heart attack in the next 10 years. With these risk scores, objective risk assessment is possible compared to what we used to assess risk in a subjective way.
For the Indian population who are having a risk of more than 10 per cent, it is considered high risk in India. This means more than 10 per cent chance of having a heart attack in the next 10 years is considered high risk in India.
Indian race and south Asian ancestry itself is a risk enhancer. If risk calculation is more than 10 per cent, it is considered high risk whereas the same for any other race, we consider high risk if it is more than 20 per cent. The bar is set at the lower level for the Indian population.
Clinical practitioners and even lay persons calculate risk score. Easiest risk score they use is by the American Heart Association. This risk score calculator is developed in the form of an app and available on Google as well as Apple store. It is an ASCVD risk calculator. This is an objective app. A person can calculate the risk.
Risk score gives an idea what medication one should take. For example whether a person should take aspirin, cholesterol lowering medication, blood pressure medication, and what lifestyle modification is required. One can also know how much risk reduction is possible by adhering to those lifestyle modifications.
Indians calculating risk on ASCVD need to choose an ‘other’ group which happens to be of South Asian ancestry. More than 20 per cent risk score is considered high risk in the American context while for Indian people, more than 10 per cent risk is considered high risk.
Book Online Consultaion
What Are the 5 Most Common Heart Problems?
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Heart disease remains a significant global health concern, accounting for a considerable number of deaths worldwide. While it is well known that factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity can contribute to heart disease.
A weak heart, also known as heart failure, is a condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood efficiently, leading to reduced circulation and inadequate oxygen supply to the body's tissues.
Complex coronary angioplasty in the heart is an advanced interventional cardiology procedure recommended for patients who have previously undergone coronary bypass surgery.
Maintaining a healthy heart is of utmost importance, and a well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. Heart disease, including heart attacks, is a leading cause of death worldwide.
TEER is a catheter-based procedure that utilizes a small, flexible device to repair the mitral valve. The procedure is typically performed in a cardiac catheterization lab under fluoroscopic guidance without the need for a sternotomy or cardiopulmonary bypass.
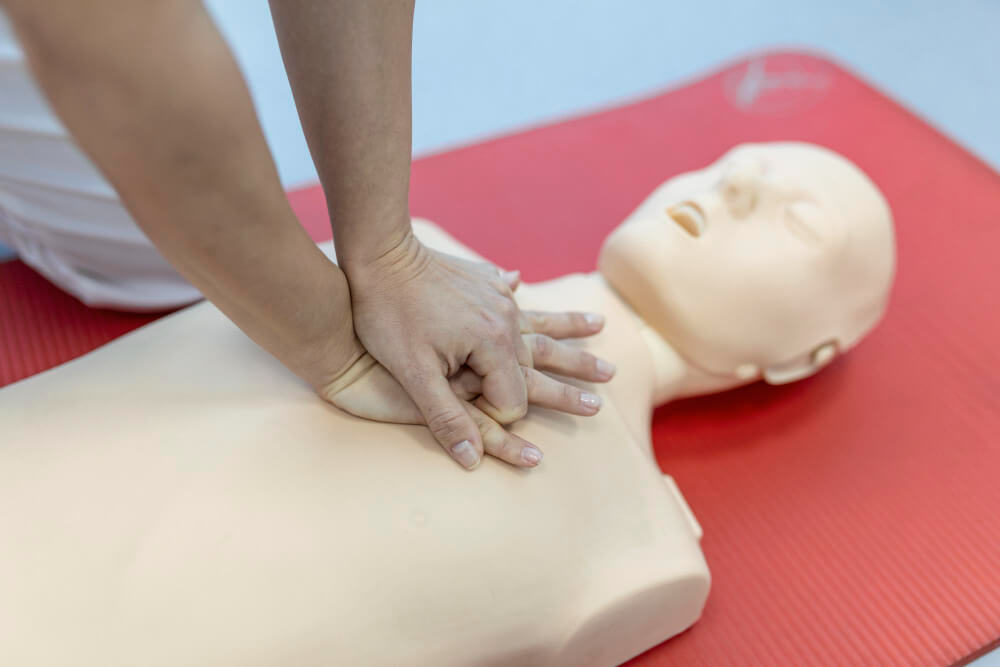
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency life-saving procedure performed on individuals experiencing cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac failure. CPR aims to manually keep the blood and oxygen flowing in the body until professional medical help arrives.