Atrial Fibrillation
Atria means the upper chambers of the heart. These upper chambers of the heart start beating chaotically – quiet irregularly – that is what is called as Atrial Fibrillation.
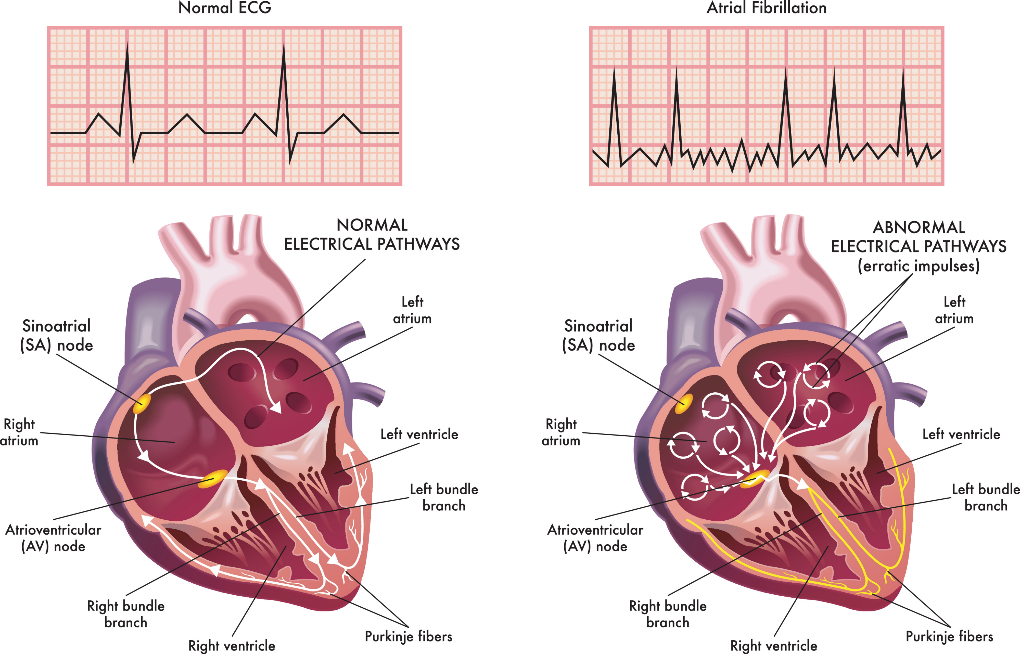
Normally a heart beats around 60-100 times per minute so the number of beats a heart should beat is determined by a structure called sinus node. This is called normal sinus rhythm. Its function is to maintain the heart rate within a particular range. But at times, when there is an atrial enlargement or infection or inflammation these atria start beating chaotically. This chaotic beating of the atria is called Atrial Fibrillation.
In this Atrial Fibrillation in contrast to the 60-100 beats per minute of the atrial contraction here the atrial rate is between 400-600 per minute so the atria start beating very fast and quiet irregularly.
So if the atria beat very fast and irregularly what does it lead to?
If the atria beat at 400-600 per minute the beating is quiet ineffective so that is what we call as atrial paralysis or the atria is not effectively functioning so atrial fibrillation leads to dysfunction of the atrium.
This atrium contributes to about 20% of heart output so when the atrium is dysfunctional the heart pumping is reduced by around 20%.
Onset of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation can be either
- Sudden onset – Acute
- Long-standing – Chronic
- Coming on and off – Paroxysmal
Acute Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial Fibrillation sometimes it happens suddenly like in the scenario of an acute heart attack or an inflammation of pericardium (inflammation of the superficial layer of the heart) or when there is a sudden pulmonary embolism (blood clots formation in the blood vessels supplying the lungs) s. In those circumstances there can be a sudden onset of Atrial Fibrillation so this is called an acute Atrial Fibrillation so once after the cause for the Atrial Fibrillation has been reversed there is a strong chance that this Atrial Fibrillation can revert back to normal sinus so the atrium will start contracting at a much lower rate.
Chronic Atrial Fibrillation: The other type of Atrial Fibrillation is a Chronic Atrial Fibrillation or a Chronic Persistent Atrial Fibrillation where the Atrial Fibrillation is present for more than a week in duration and continues to persist. So that means that the Atrial Fibrillation does not come back to sinus rhythm but in fact is present for beyond a week and continue to remain so for rest of the life so that is what we call as Chronic Atrial Fibrillation or a long standing Atrial Fibrillation.
Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: There is another type of Atrial Fibrillation called Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation that means Atrial Fibrillation is present for certain duration of time and then reverts back to sinus rhythm and once again might come up again. It comes and goes that is what we call as Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation.
Which type of Atrial Fibrillation is dangerous?
All types of Atrial Fibrillation are dangerous.
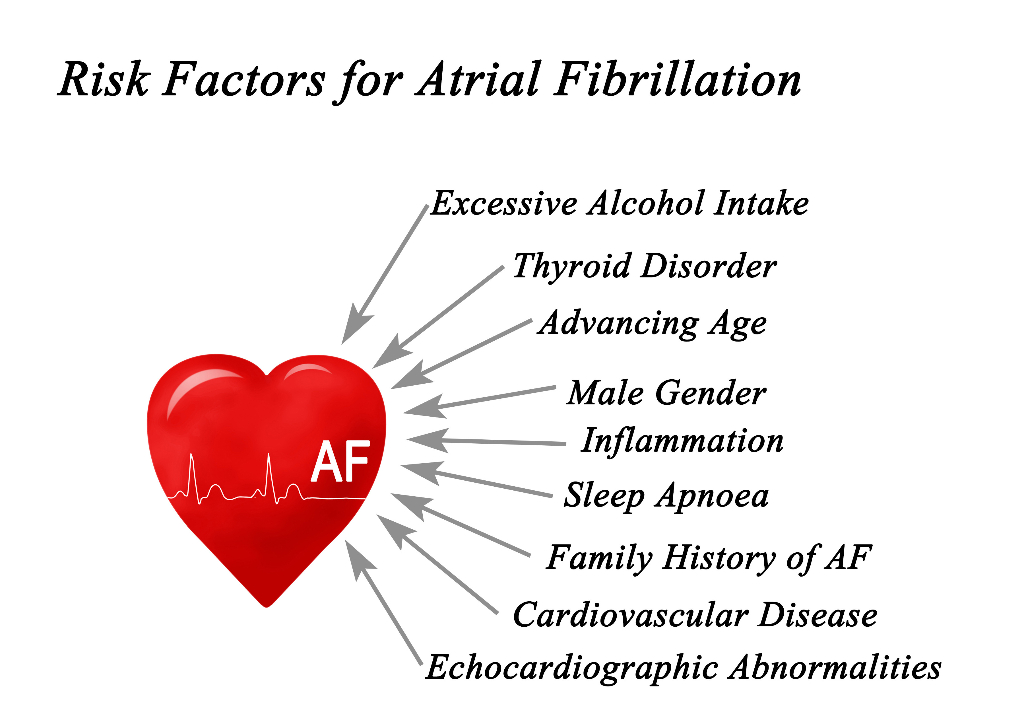
Why is atrial fibrillation dangerous?
Atrial Fibrillation as we understood reduces the pumping ability of the heart by 20%. In addition, a prolonged and fast rate of the heart fatigues the heart and reduces the heart’s pumping efficiency. This is called left ventricular dysfunction.
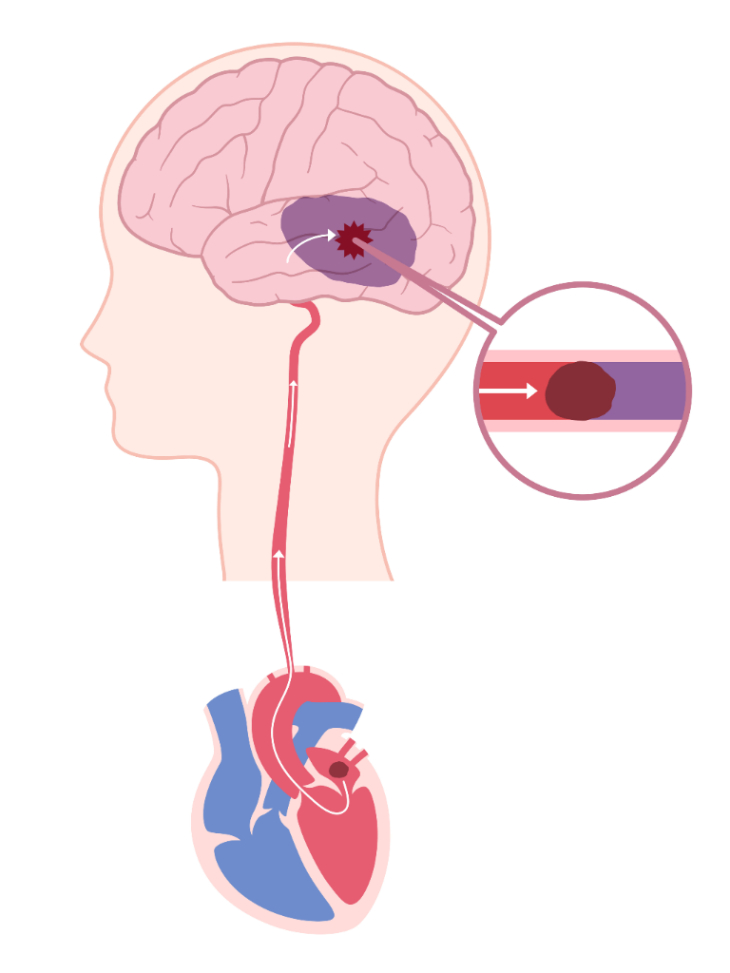
The most dreaded complication of Atrial Fibrillation is brain stroke. The chaotic contraction of atria leads to inefficient cardiac contraction. This inefficient contraction leads to pooling of blood within atrium which can potentially lead to formation of blood clots in the atrial chambers.
These blood clots which are present in the atrial chamber can get dislodged and potentially lead to a brain stroke.
So a patient with Atrial Fibrillation
- can develop a heart dysfunction
- can develop a brain stroke
- can develop a sudden reduction in the heart output
How can we detect Atrial Fibrillation?
We have seen that if the Atrial Fibrillation is chronic and persistent that can be easily detected by an ECG or an Electrocardiogram. This is the simplest inexpensive test to detect the presence of Atrial Fibrillation.
But if it is a Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (that means it comes and goes) then we might have to use a long term ECG recording technology to identify or diagnose or detect the presence of Atrial Fibrillation.
There are numerous technologies to identify Atrial Fibrillation on a long standing basis.
External devices
- Patch ECG
- Holter monitoring
- Novel devices like the Alivecor where one can detect atrial fibrillation from finger tip ECG.
A number of technological advances have appeared to detect the presence of Atrial Fibrillation. Even our Apple watch also has got an Atrial Fibrillation detection algorithm so an apple watch also can detect the presence of Atrial Fibrillation. Quite a few of my patients tend to identify their Atrial Fibrillation from their apple watch so you have got simple technologies you have got complex technologies

Internal device
Implantable Loop Recorder:
The most complex technologies like where you can put an implantable loop recorder. A small device is implanted into the subcutaneous tissue that means beneath the skin and the muscle or the fat and then this recorder will continue to record the heartbeat.
So you have got the simple technology like the ECG and a moderately complex technology like the ECG patch or the Holter recording or a 14 day ECG patch is also available and finally for those patients where the Atrial Fibrillation is very rare you can put an implantable loop recorder that can last for about 2 years of the time.

