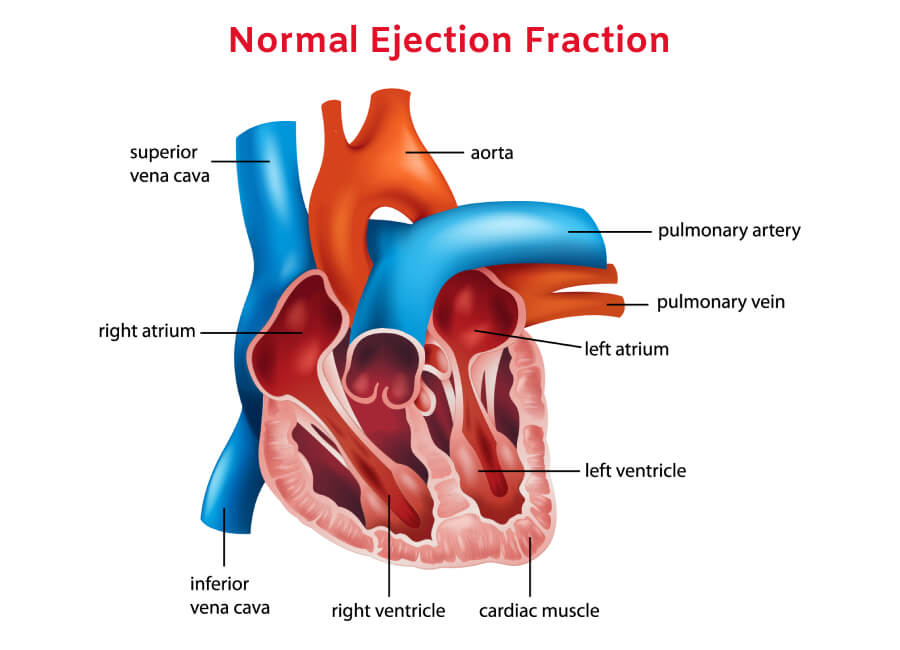
A weak heart, also known as heart failure, is a condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood efficiently, leading to reduced circulation and inadequate oxygen supply to the body's tissues.
cardiomyopathy | Dr Raghu
Congestive heart failure is characterized by a gradual deterioration in the heart’s ability to pump blood throughout the body. It can result in various symptoms, such as swelling in the abdomen, feet, and legs, shortness of breath, fatigue
Heart failure refers to a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood throughout the body with maximum efficiency. It’s usually the result of progressive weakening, thickening, or stiffening of the heart muscles.
Heart failure is a common condition with no known cure. However, proper treatment can control the disease progression and thus improve a patient’s quality of life and longevity. To decide the proper course of treatment, a doctor must first determine the type of heart failure a patient has developed.
Depending on the part of the heart’s pumping cycle that’s been affected, heart failure can be of two types – diastolic and systolic. You can learn more about the symptoms, causes, treatment of diastolic dysfunction and differentiation from systolic dysfunction in our previous article.
In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into systolic heart failure and understand its causes and symptoms.
Systolic Heart Failure: A Closer Look
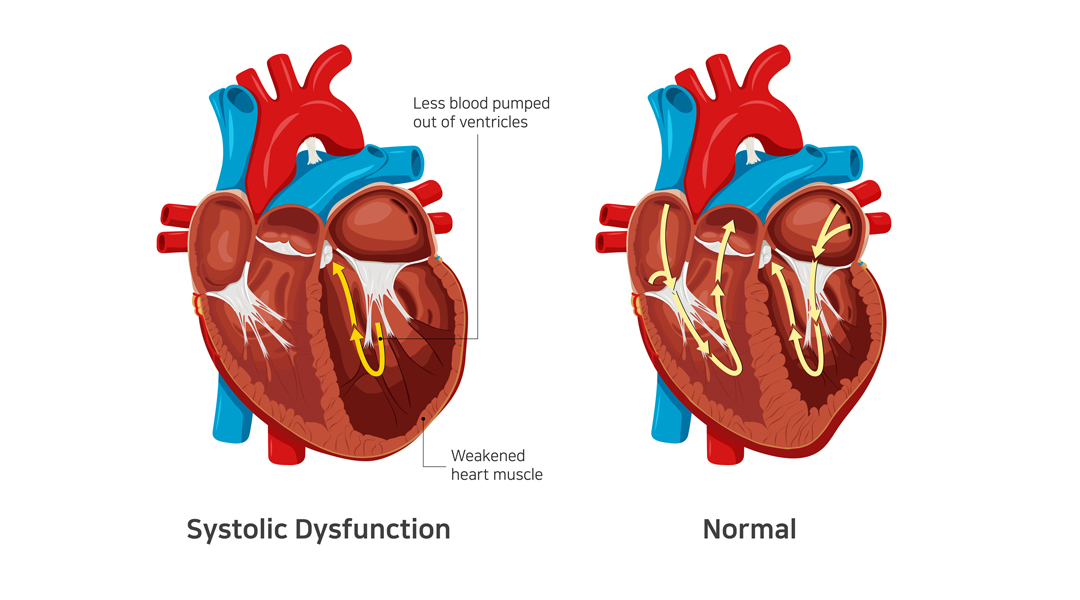
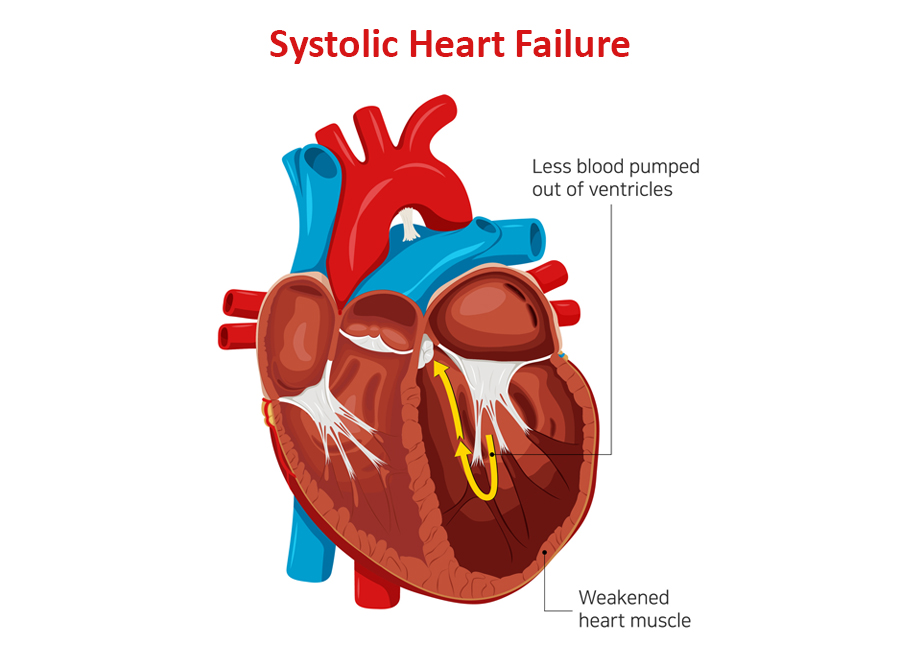
Systolic heart failure occurs due to a problem in the heart’s contraction (or systolic) phase. It’s characterized by stretching and weakening of the left ventricular muscle, due to which the heart pumps out less oxygenated blood to the body.
It’s also known as heart failure with reduced ejection infraction. As the condition worsens, it can also weaken the right ventricle and take a toll on its pumping power too.
Related: What Are the Symptoms of Diastolic Dysfunction?
Causes of Systolic Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure is caused by underlying medical conditions that damage the left ventricle. The most common causes include :
- Hypertension (the left ventricle has to use increased pressure to pump blood through the body)
- Coronary artery disease (buildup of cholesterol in the arteries) – with or without a heart attack.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (weakening of the left ventricle due to an infection or long-term exposure to alcohol and narcotics)
- Abnormal heart rhythm (also known as atrial fibrillation)
- Previous heart attack
Additionally, people who are older or have diabetes are at a higher risk of developing systolic heart failure.
Related: Understanding Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms
Symptoms of Systolic Heart Failure
In systolic heart failure, an adequate amount of oxygen-rich blood doesn’t reach all organs. The most common indicator of the condition is a lower ejection fraction.
It can result in the following symptoms:
- Breathlessness – initially on exertion and in later stages even at rest or lying down.
- Swelling of feet, face, abdomen – due to fluid accumulation in various organs
- Engorged and pulsatile neck veins
- Confusion (due to a lack of oxygen supply in the brain)
- Weight gain (due to a buildup of excess fluid in the body)
- Fatigue (due to reduced blood supply to the muscles)
- Pale or bluish skin tone (due to restricted blood supply to the skin and other vital organs).
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Typically, a doctor prescribes various tests, such as chest X-ray, ECG, and echocardiography, to diagnose systolic heart failure and its root cause. The treatment plan depends on the underlying cause.
In most cases, systolic heart failure is treated using one or more of the following medications:
- Beta-blockers
- Diuretics or water pills
- ACE inhibitors
- Digoxin
- Anticoagulants
Additionally, doctors recommend a healthy diet and lifestyle changes to improve cardiac health and manage underlying conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes.
Related: Diagnosing Congestive Heart Failure
In Conclusion
If left untreated, systolic heart failure can damage vital organs and even lead to death. It’s crucial that patients watch out for symptoms like swollen feet, mental confusion, and bluish skin color and seek medical treatment at the earliest.
Dr. C Raghu is an experienced cardiologist who specializes in interventional cardiology and TAVR. If you or anyone you know is experiencing symptoms of systolic heart failure, connect with Dr. Raghu for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Book Online Consultaion
What Is Systolic Heart Failure ? – Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
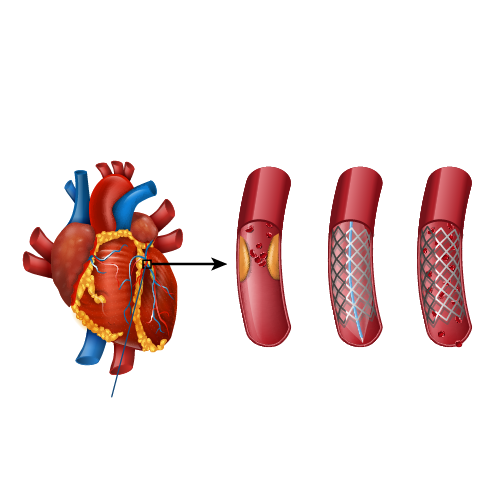
Angioplasty
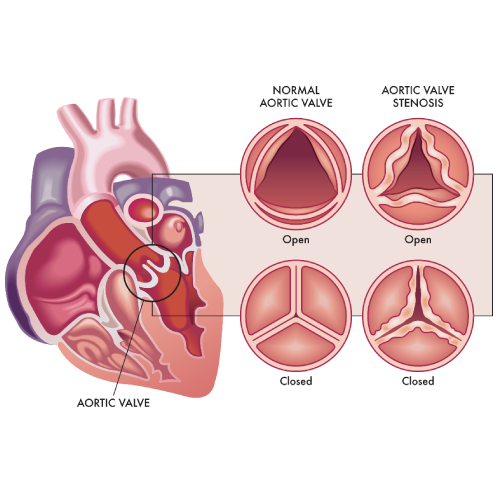
Aortic Stenosis
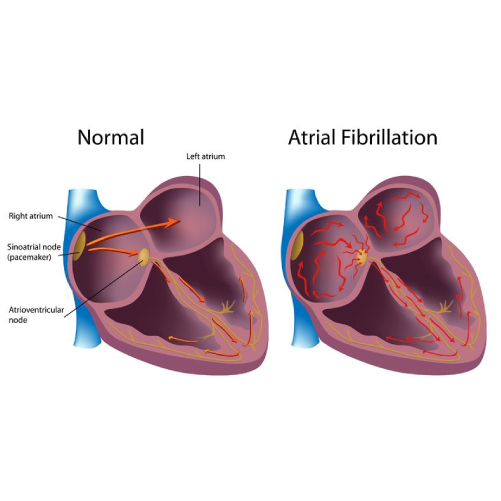
Atrial Fibrillation
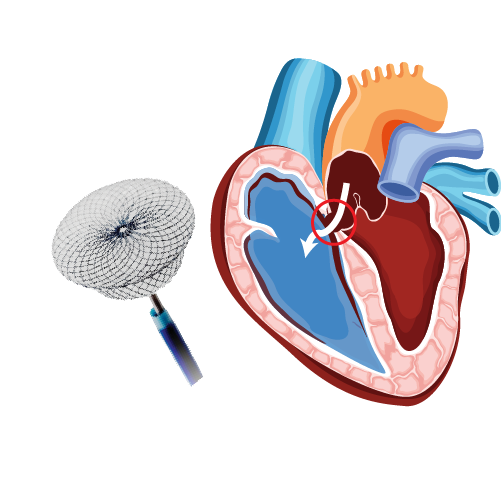
Atrial Septal Defect
The ejection fraction is one of the most common parameters used to diagnose heart failure. If you want to know more about the cause, symptoms, and types of heart failure, check out our previous blog posts.
The heart is a critical organ that powers the human body. It beats roughly 100,000 times a day and pumps more than 2,000 tons of blood throughout the body.
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart gradually loses its pumping capacity. It can lead to symptoms like breathlessness, fluid buildup, and mental confusion. In the long run, it can result in organ damage and even death.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the symptoms, causes, and treatment of congestive cardiac failure. Let’s dive right in.
Congestive Cardiac Failure and Heart Failure: Are They the Same?
Traditionally, doctors used the terms congestive cardiac failure or congestive heart failure to refer to the progressive deterioration of the heart’s pumping action. They used “congestion” to describe the buildup of fluid in the lungs due to heart failure.

However, subsequent studies have shown that the condition can lead to other symptoms, such as swollen feet, fatigue, and mental confusion. That’s why doctors use the term heart failure nowadays.
Causes of Congestive Heart Failure
Irrespective of whether you call it congestive cardiac failure or simply heart failure, its most common causes include:
- Heart valve damage
- Diabetes
- Heart rhythm disturbances
Additionally, damaged or dying heart tissue due to an infection or a previous heart attack can result in congestive cardiac failure.
Related : Mitral Valve Stenosis : Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure
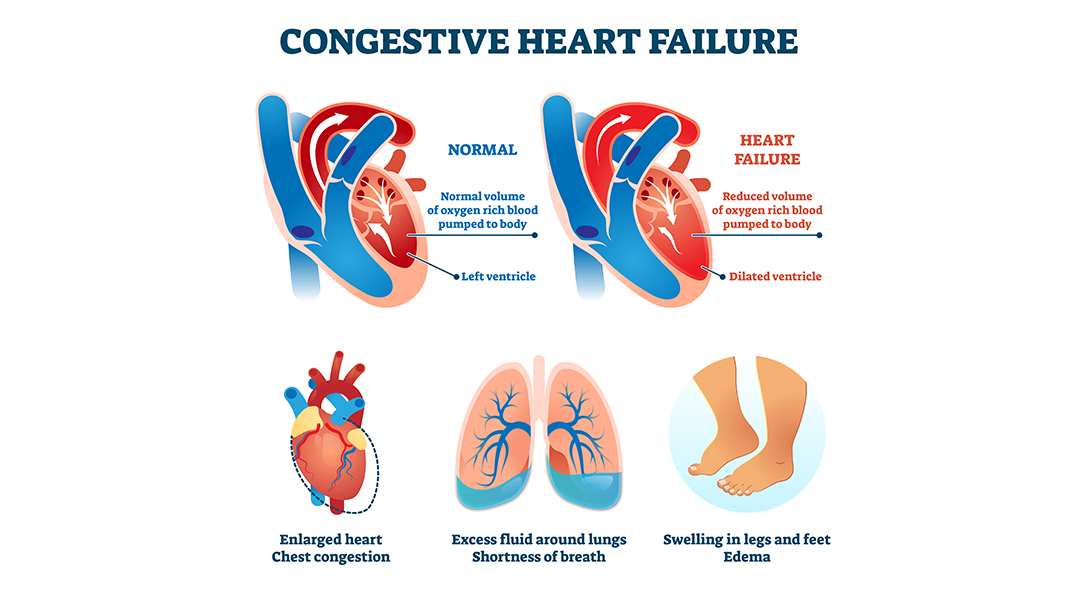
The symptoms of congestive heart failure depend on whether it causes a lack of oxygen supply to the organs or excess fluid buildup in the body.
In the first case, the symptoms include mental confusion, fatigue, and discolored or bluish skin. In the second case, heart failure can lead to symptoms, such as shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, weight gain, swelling in the feet, legs, and abdomen, and loss of appetite.
Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure
The treatment of congestive heart failure depends on its underlying cause and the side of the heart that’s affected. A doctor will order a series of tests, such as chest X-ray, ECG, echocardiogram, and coronary angiography. Routine blood tests, such as lipid panel and electrolyte tests, might be needed, too.
Once the root cause is identified, your doctor can prescribe one or more of the following medications:
- Diuretic or water pills
- Beta-blockers
- ACE inhibitors or Angiotension receptor Neprilysin inhibitor
- Digoxin
- Anticoagulants
Additionally, the doctor will recommend lifestyle changes, including exercise, a low-sodium diet, and weight loss. Also, they’ll ask you to quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption. In extreme cases, patients need a heart transplant or ventricular assist device (VAD) to improve their quality of life.
Wrapping Up
Congestive cardiac failure is a chronic condition with no known cure. If left untreated, it can lead to organ damage and death. However, a proper treatment plan comprising lifestyle changes and medications can help manage various symptoms.
Dr. C Raghu is a renowned cardiologist and a specialist in interventional cardiology. If you or anyone you know is experiencing symptoms of heart failure, don’t hesitate to contact Dr. Raghu right away.
Book Online Consultaion
Congestive Cardiac Failure – Blog
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases

Angioplasty

Aortic Stenosis

Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial Septal Defect
Heart failure can be categorized into different types depending on various factors. While most conditions cause similar symptoms, clear identification of the type of heart failure is crucial for doctors to determine the proper course of treatment.
Heart is a complex organ and can get affected by diseases that can affect various systems of the heart. The common heart ailments that would be observed include:
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) – accumulation of cholesterol plaques within the walls of the blood vessels (coronary arteries) supplying the heart. This leads to obstruction to blood flow of the heart that can cause chest pain or heart attack.
Valvular heart disease: Heart valves are flap-like structures akin to doors between rooms. They control the blood flow between various chambers of the heart. They play a key role in blood circulation.
There are four valves in the heart
- mitral and aortic valves on the left side of the heart
- tricuspid and pulmonary valves on the right.
These valves can either get narrowed (stenosis) or get “leaky” (regurgitation).
Cardiomyopathy: This disease affects the heart muscle leading to inefficient heart pumping efficiency. Cardiomyopathy can be either due to:
- Direct heart muscle diseases – Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy.
- Indirect heart muscle diseases –
- Consequent to
- heart attack (ischemic cardiomyopathy)
- infective (myocarditis) and
- heart rhythm problems
- Consequent to
- Heart Rhythm problems (Arrhythmias)- Normal heart rate is between 50-100 beats per minute. The maintenance of heart rhythm within a specific range is possible due to an efficient electrical system of the heart also called the conduction system.
- Slow heart rate – Bradycardia usually due to retardation of conduction within the conduction system of the heart. The most common cause is due to age related degeneration of the conduction system. The garden variety disease causing slow heart rate is called complete heart block.
- Fast heart rate – Tachycardia in this disease there is an accelerated conduction of electrical impulses – if the fast heart arises in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) it is called ventricular tachycardia if it arises in the upper chambers (atria) of the heart it is called supraventricular tachycardia.
Doctors usually recommend a battery of tests based on the system of the heart that has been affected. Based on a detailed history followed by a detailed physical examination, appropriate battery of tests would be suggested. The diagnosis of the heart ailment is critically dependent on the results of tests.
In addition to confirming the diagnosis, test results might indicate the disease complications and thus your doctor is able to stage the disease and the possible outcomes.
Related : Basics about Heart Failure
Blood tests:
- Complete blood count (CBC): A complete blood count helps to detect infection, anaemia and other blood disorders. Anaemia is a common finding in heart failure, plus it also contributes to worsening of heart failure. A low platelet count may be caused by medications such as diuretics or heparin.
- Cardiac troponins (cTn1, cTnT, high sensitivity troponins): It is an important blood biomarker useful for the detection and predicting outcomes of chest pain or heart attack. Cardiac troponins may also be high in other heart related conditions like acute myocarditis, coronary vasospasm and non-cardiac conditions (e.g. sepsis, chronic kidney disease).
- Electrolytes, urea and creatinine: Assessment of kidney function is essential in all cardiac patients. Both kidney and cardiac disease share the same risk factors and either disease can lead to poor outcomes of the other disease. In addition, cardiac drugs’ doses need to be modified considering the kidney function.
- Liver function tests:: Certain drugs such as statins and amiodarone, which are commonly prescribed for patients with heart disease, can trigger liver failure. Liver failure could also be a consequence of heart failure.
- Thyroid function test: Medication for heart disease like amiodarone may cause hyper or hypo thyroidism. Altered thyroid hormone can also cause heart dysfunction and responsible for coronary artery disease.
- Brain Natriuretic Peptides (BNP or N-terminal pro BNP): BNP is a useful tool to differentiate between cardiac and non-cardiac causes of shortness of breath. High levels of BNP and N terminal pro BNP is associated with increased severity of heart disease and greater risk of hospitalization.
Related: Types of Heart Failure
Electrocardiography(ECG):
This test detects and records the electrical activity of the heart. This is a simple, non-invasive test which is very useful to determine abnormalities in the heart rate, rhythm and to identify risk of damaged heart muscle or other structural changes in the heart. This test detects the presence of arrhythmias and coronary artery disease.
Exercise stress testing:
Exercise makes your heart work harder. Exercise stress testing is done either on a treadmill or cycle ergometry with the patient connected to an electrocardiogram. Exercise stress testing may identify myocardial ischaemia, haemodynamic/ electrical instability, or other exertion-related signs or symptoms. When an individual is not able to exercise, medications are given to stress the heart and the response is evaluated.
Chest X-ray:
Chest X ray is very useful to differentiate whether shortness of breath is due to a respiratory disease or heart disease. It can also help in detecting complications of heart failure such as cardiomegaly, interstitial oedema, pulmonary oedema and pleural effusions.
Coronary angiography:
Coronary angiography is useful to determine the health of the coronary arteries. In this test, a catheter is inserted into the coronary arteries and a dye is injected to produce clear X ray images of the coronary arteries. This helps to find out the presence, location and extent of vessel narrowing. The results also help to decide which type of treatment would be most appropriate for correction of heart problem.
Echocardiography:
This test gives an ultrasound image of the heart. Echocardiography can provide information about the size and shape of heart chambers, blood flow velocities, heart muscle function when they contract and relax, abnormalities of the movement of the heart wall, valve function, and presence of thrombus (blood clot) in the heart.
Stress echocardiography helps in detecting decreased blood flow to heart during exertion. In this test, echocardiography is done immediately post stress. The stress can be exercise or could be induced by medications.
Myocardial perfusion scanning (MPS):
MPS is a non-invasive test which helps to determine how well blood flows through your heart muscles. In this test, a small amount of a radioactive substance is injected into the blood. The test evaluates the severity of coronary artery disease and provides guidance regarding the need as well as success of invasive procedures like angioplasty and stent insertion.
Cardiac Computerized Tomography (CT):
Cardiac CT provides detailed images of the heart. This helps to identify structural abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels such as aneurysms, valve dysfunction and damage to the pulmonary vasculature. Cardiac CT also provides information about patency of grafts following coronary artery bypass graft.
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Cardiac MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency to provide detailed 3D images of the heart and surrounding structures. The image provides accurate information about cardiac volumes, muscle mass, contractility, and how efficiently the heart is pumping. Like cardiac CT, cardiac MRI also helps to provide information about patency of grafts following coronary artery bypass graft.