Understanding Coronary Artery Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Coronary artery disease (CAD), commonly known as coronary heart disease or simply heart artery disease, is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening cardiovascular condition. It occurs when the coronary arteries, responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow.
In this article, we will delve into the causes, risk factors, symptoms, complications, and treatment options of coronary artery heart disease.
Causes and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease
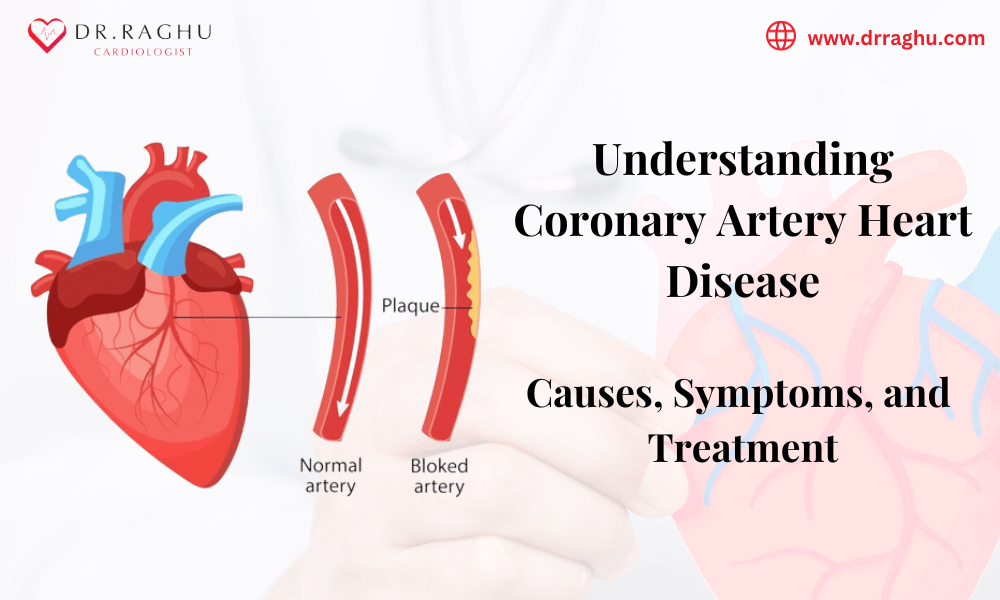
CAD primarily develops due to atherosclerosis, a process where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances accumulate on the inner walls of coronary arteries. That, in turn, leads to the formation of plaque. It can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle and lead to various complications.
The following factors increase the risk of developing CAD:
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage the lining of blood vessels, contributing to atherosclerosis.
- Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure puts added stress on the coronary arteries, making them more susceptible to damage.
- High cholesterol levels: An excess of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the blood increases the risk of plaque formation.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes have a higher risk of developing CAD due to elevated blood sugar levels that can damage blood vessels.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, both of which are CAD risk factors.
- Family history: A family history of CAD can indicate a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- Age and gender: The risk of CAD increases with age. Men are generally at a higher risk than women, although women’s risk rises after menopause.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of regular exercise contributes to obesity and increases CAD risk.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Heart Disease
The symptoms of CAD can vary widely and may not always be apparent until the disease has progressed. Common symptoms include:
- Angina: Chest pain or discomfort, often described as a squeezing or pressure-like sensation. It is typically triggered by physical activity or emotional stress.
- Shortness of breath: Especially during physical activity or when lying down, this can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness, often associated with CAD, as the heart struggles to pump blood efficiently.
- Other symptoms include pain in the arms and shoulders, lightheadedness, and general weakness. Many patients also report breaking into a cold sweat.
Coronary Artery Disease Complications
Heart artery disease can lead to several complications, which can quickly turn life-threatening. The most common complications include:
- Heart attack: When blood flow to a part of the heart is completely blocked, it can result in a heart attack, causing damage to the heart muscle.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms can develop due to CAD, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like ventricular fibrillation.
- Congestive heart failure: CAD can weaken the heart, reduce its ability to pump blood effectively, and ultimately lead to congestive heart failure.
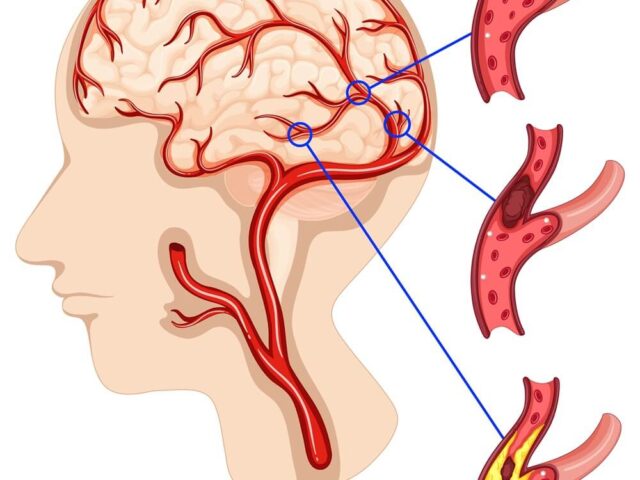
- Stroke: CAD increases the risk of blood clots forming in the coronary arteries, which can break free and travel to the brain, causing a stroke.
Coronary Artery Disease Treatments
Managing CAD involves addressing risk factors, alleviating symptoms, and preventing complications. Heart artery disease treatment options include the following:
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels and manage diabetes. Aspirin and other blood-thinning medications can help reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: It combines exercise, education, and counseling to help individuals recover from a heart attack, manage symptoms, and improve overall heart health.
- Interventional procedures: In cases of severe blockages, procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement can help restore blood flow to the heart.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): This surgical procedure involves rerouting blood around blocked arteries using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, complications, and treatment options is crucial for managing this chronic disease effectively.
By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, seeking medical advice, and adhering to prescribed treatments, individuals can reduce their risk, alleviate symptoms, and improve their overall quality of life while living with CAD. Regular check-ups and early intervention are key to managing this condition and preventing its serious complications.
Dr. C Raghu is a renowned heart specialist who is regarded as the best cardiologist in Hyderabad. If you or anyone you know is looking for effective heart artery disease treatment, feel free to reach out to Dr. Raghu today.
Book Online Consultaion
Understanding Coronary Artery Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Subscribe the Hearty Life Blogs

DR. RAGHU | Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad
Cardiology Coronary, Vascular and
Structural Interventions
Conditions & Diseases
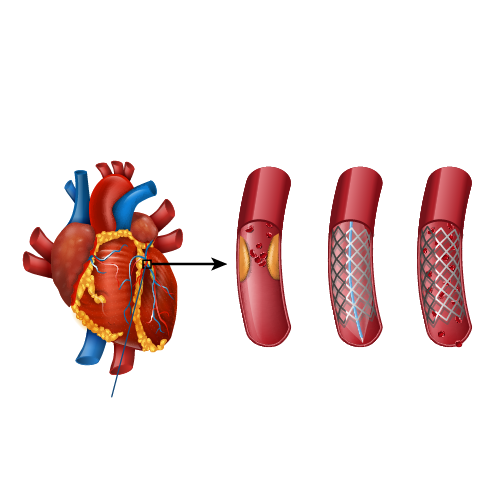
Angioplasty
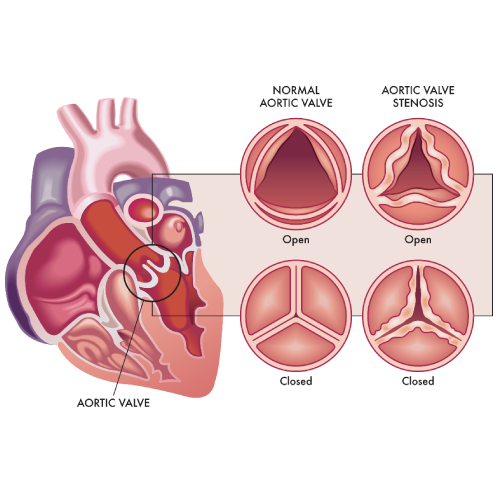
Aortic Stenosis
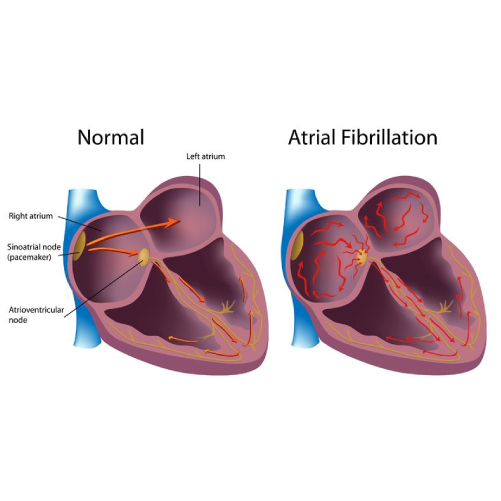
Atrial Fibrillation