VSD Device Closure
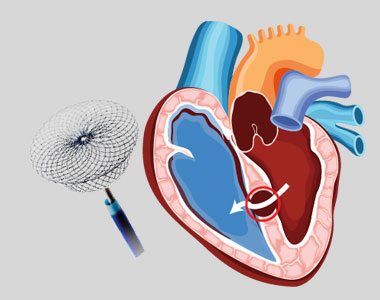
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart condition in which the opening between the pulmonary artery and the aorta, persists after its normal closure time. The ductus arteriosus is a small connection between the two major blood vessels in the fetal heart, and it naturally closes shortly after birth. When it fails to close, it’s called patent ductus arteriosus.
A PDA may allow the oxygenated blood to mix with the deoxygenated blood, compromising the heart and lung function.
What are the treatment options for PDA?
- The treatment options depend on the age of the person.
- In a premature baby, the PDA may close with time, as the baby grows. Some babies may need medications such as indomethacin, to facilitate closure. Surgery may be needed if the duct fails to close.
- In full-term babies, a small defect can be monitored, as it may close with time. Large defects may need to be closed surgically.
- Surgical closures can be achieved through open-heart surgery and percutaneous catheterization.
What is Device Closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
The larger PDA results in increased workload of heart, and also carries a risk of bacterial infection. PDA can be closed by inserting a device through the blood vessel in groin, a non-surgical method called percutaneous transcatheter approach.
Who is eligible for this treatment?
This method is considered only if the child is
- Older than 6 months
- At least 22 pounds
- With defects that are not too large
Considerations in adults include:
- The device closure is considered as long as the elevated pressure in the lungs is not irreversibly elevated
- If the lung pressure is already very high, it is carefully measured along with lung resistance to determine the safety the procedure.
What are the risks associated with the procedure?
PDA closure is a low risk procedure, but the common risks include:
- Rupture of the blood vessel or the heart wall
- Complications during positioning the device
- Leakage through the closure device
What happens during the procedure?
- In case of adults, a sedative might be given to relax them, and a local anesthetic is given to numb the site of catheter introduction.
- Children are administered general anesthesia during the procedure.
- A catheter is inserted into the blood vessel in the groin. It is then moved up to the heart into the PDA.
- The pressure, oxygen saturation and the size of opening in the heart is measured.
- A closure device is threaded through the catheter and placed onto the PDA.
- Once the device is in place, it is pushed out of the catheter to implant it over the opening.
What care should be taken post-procedure?
- After implantation, the catheter is removed, and the incision is closed.
- The procedure usually takes between 1 and 3 hours.
- You might need to have an X-ray after the procedure to ensure the implant is at the right position.
- An echocardiogram may be recommended after six months to ensure that the PDA is properly closed.
- Antibiotics might be prescribed to prevent endocarditis.
- The child may need to come for regular follow-ups to ensure that the device closure is effective.
- Conditions
- Acute limb ischemia
- Chronic limb ischemia
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve regurgitation
- Atrial fibrillation
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Myocarditis
- Endocarditis
- Pericarditis
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cath lab procedures:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Primary Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty
- CHIP Angioplasty
- Aortic valve replacement surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery
- Device closure for Atrial septal defect
- Device closure for Ventricular septal defect
- Device closure for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter
- LA appendage closure
- Fistuloplasty
- Balloon mitral valvotomy
- 24 hours emergency services
- Clinics- weekly basis/monthly basis/ Yearly basis
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Diagnosis


